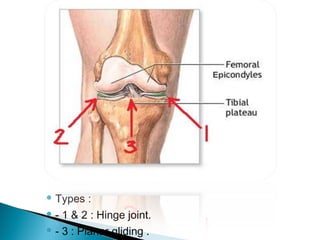
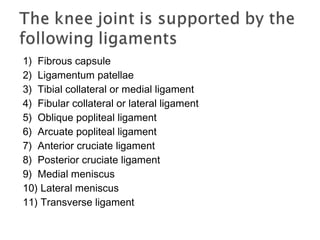
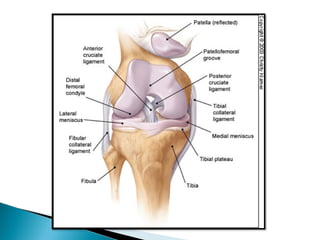
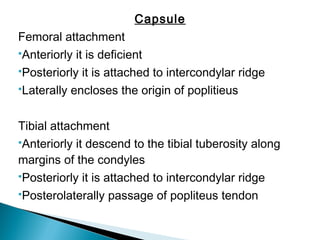
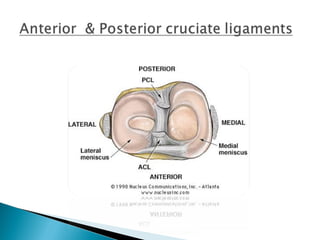
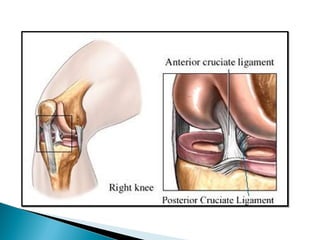
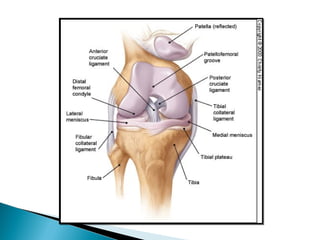
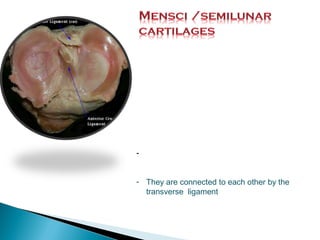
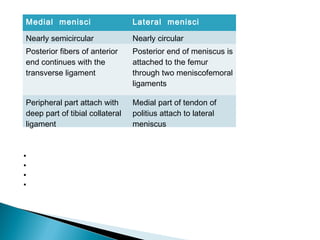
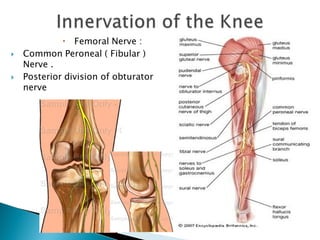
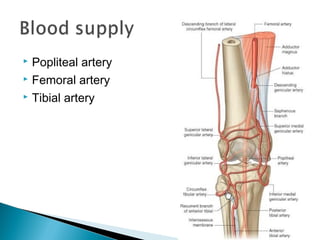
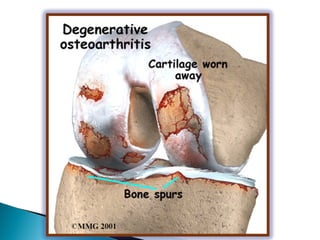
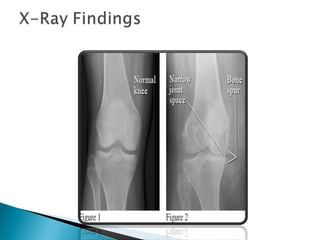
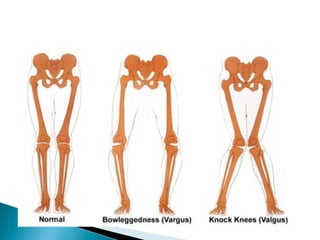
The knee joint is composed of three joints within a synovial cavity. It includes the medial and lateral condylar joints between the femur and tibia, and the patellofemoral joint between the femur and patella. The knee joint is supported by ligaments including the ACL, PCL, medial collateral ligament, lateral collateral ligament, and menisci. The knee allows for flexion and extension through the actions of various muscles and is an important weight-bearing joint that can be subject to injuries and osteoarthritis.