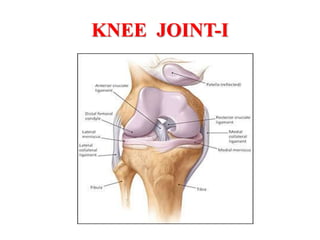
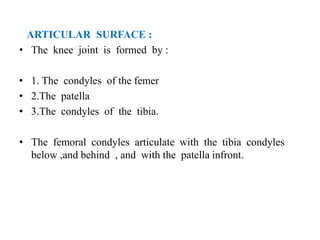
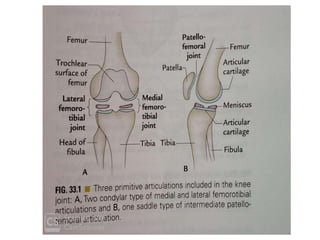
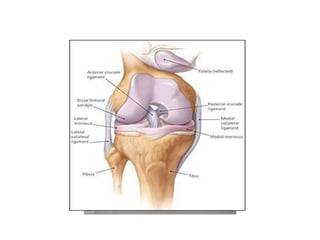
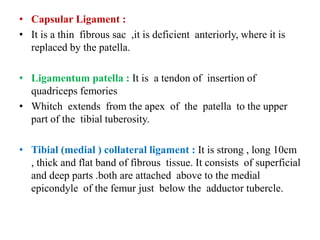
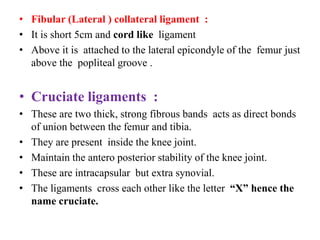
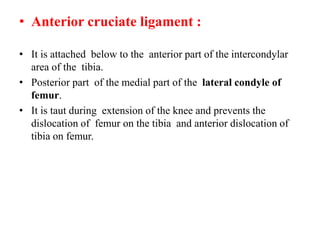
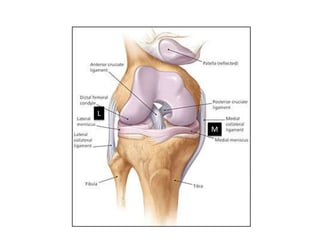
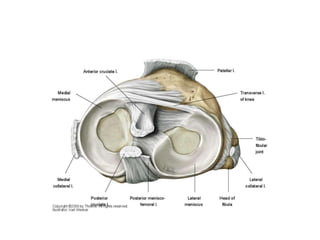
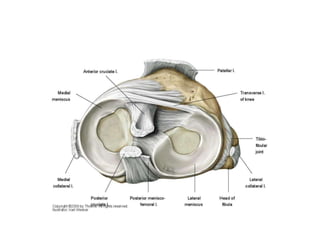
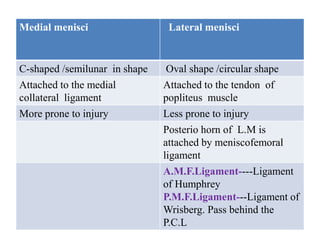
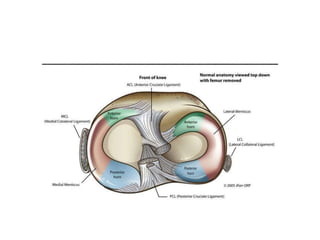
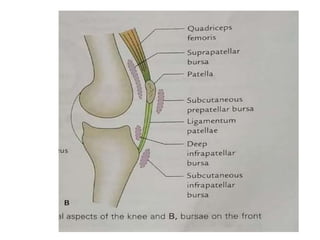
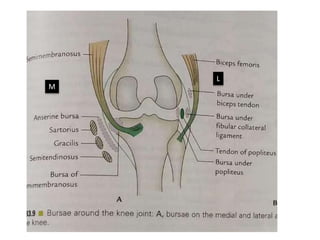
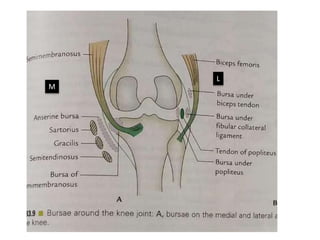
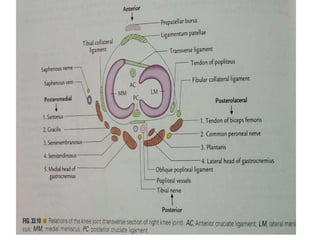
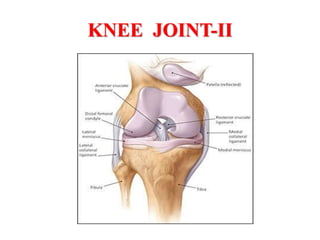
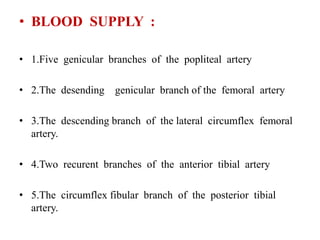
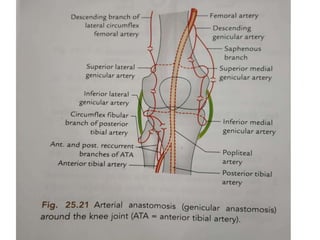
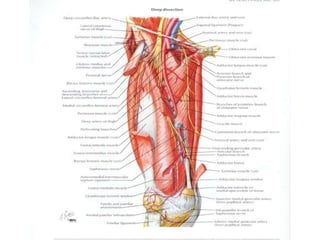
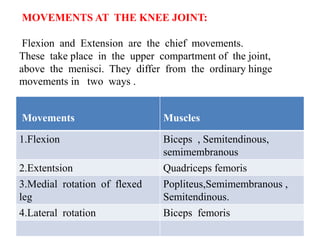
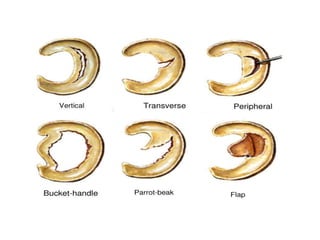
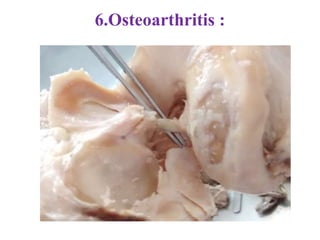
The knee joint is the largest and most complex joint in the body, formed by the fusion of three joints. It contains articular surfaces on the femur, patella, and tibia. Stability is provided by muscles, collateral ligaments, and cruciate ligaments. The knee allows for flexion, extension, and medial/lateral rotation. Locking and unlocking during walking is enabled by the quadriceps and popliteus muscles respectively. Injuries like meniscal tears and dislocations are clinically relevant.