Embed presentation
Downloaded 59 times


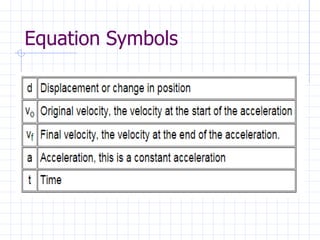
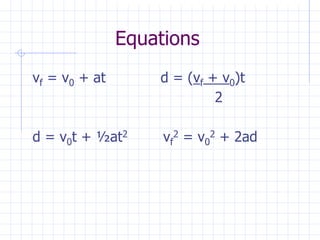




The document discusses kinematic equations, which describe motion without considering its causes. It presents four equations that can be used to determine unknown values like velocity, acceleration, displacement, and time, given other known values. These equations can model constant velocity or constant acceleration motion. Examples show how to apply the equations to calculate final velocity, distance traveled, initial velocity, and other values in scenarios involving cars, kicked balls, sledding, and road rage.








