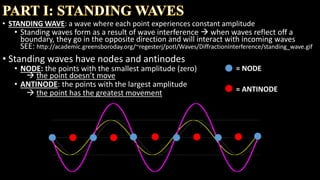
Standing waves form from wave interference when waves reflect off a boundary and interact with incoming waves. They have nodes of smallest amplitude where there is no movement, and antinodes of largest amplitude with greatest movement. Chladni figures are patterns that result from vibrations on a plate and can be explained by standing wave interference. When waves reach the end of the plate they reflect back, interfering to form nodes where sand does not move and antinodes between with movement. Higher harmonics have more complex node patterns.