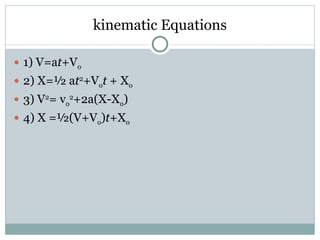
The document discusses kinematic equations and examples of their use. It introduces four common kinematic equations used to relate variables like displacement (x), velocity (v), acceleration (a), and time (t). It then provides examples of using the equations to solve for unknown variables, like using the kinematic equation relating displacement and time to find how far a ball rolls down a ramp before slowing. It also discusses free fall as a special case and provides an example of using the kinematic equations to find the time for an object to fall halfway from the top of a building.