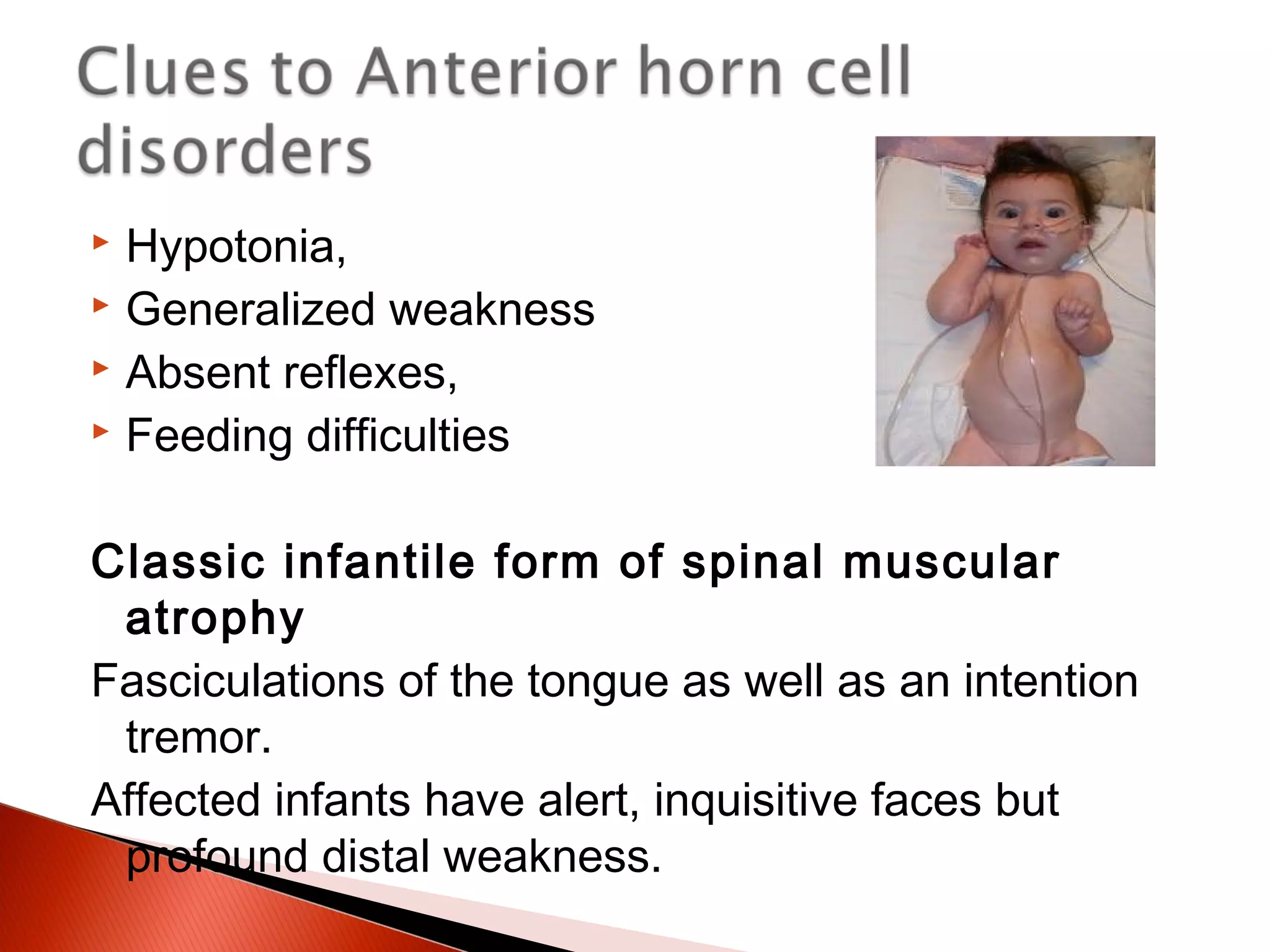
The document provides information on the evaluation of hypotonia in infants. It discusses that hypotonia can be caused by central or peripheral nervous system disorders. The most common central cause is hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, while the most common peripheral causes are congenital myopathies and spinal muscular atrophy. A thorough history, physical exam, and testing are needed to determine the underlying cause, which guides management and prognosis. The evaluation involves assessing tone, strength, reflexes and other features to localize the problem and rule out various disorders through laboratory and imaging studies.