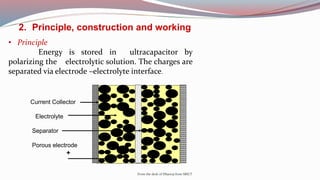
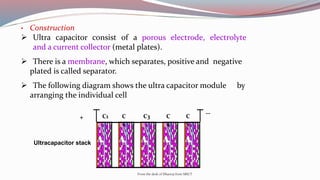
The document discusses ultracapacitors, also known as supercapacitors. It explains that ultracapacitors store energy electrostatically through a double-layer capacitance effect at the electrode-electrolyte interface, without chemical reactions. They have a high surface area porous carbon electrode, electrolyte, and separator. When voltage is applied, ions are absorbed from the electrolyte onto each electrode surface. Ultracapacitors provide higher power density and longer lifespan than batteries, but lower energy density. Their applications include electronics, electric vehicles, and backup power systems.