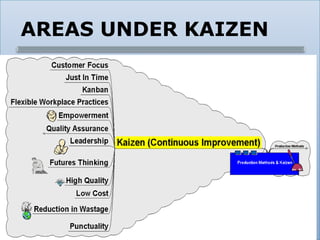
Kaizen refers to continuous improvement practices focused on processes. It originated from Japanese meanings of "change" and "good". Areas of focus for Kaizen include the "5 S's": sorting, simplifying, sweeping, standardizing, and sustaining. Quality circles involve voluntary employee groups that meet regularly to discuss and solve work-related problems. They are intended to improve quality through employee participation. While some companies have successfully implemented quality circles, challenges can include inadequate training, resistance to change, and lack of empowerment for circles to make decisions. Tata Steels in India has grown its quality circle program significantly over the years with over 7500 circles now involving 96% of employees.