Embed presentation
Download to read offline







![Coding
• P1=[8 56 96];
• Q1=[1 4 9 10];
• Sys=tf(P1,Q1)
• Roots(P1);
• Roots(Q1);
• pzMAP(sys);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varuncontrolppt-160514063421/85/k12020-control-theory-ppt-9-320.jpg)

![Coding.2
• Num=[49];
• Den=[ 1 4 9 ];
• Sys=tf(num,den);
• load ltiexamples
• ltiview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varuncontrolppt-160514063421/85/k12020-control-theory-ppt-11-320.jpg)

![Coding
• Num=[49 89 96];
• Den=[1 4 9];
• Sys=tf[Num,Den];
• Load ltiexamples
• ltiview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varuncontrolppt-160514063421/85/k12020-control-theory-ppt-13-320.jpg)

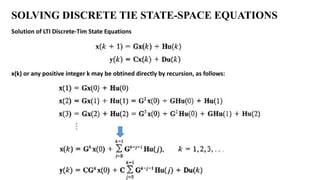
The document discusses state space representations and solutions of discrete-time state space equations. It describes how the state at any time k can be obtained directly by recursion using the state space equations. It also introduces the concept of the state transition matrix, which allows writing the solution as a matrix exponential involving the state transition matrix. Finally, it discusses using the z-transform approach to solve discrete-time state equations.








![Coding
• P1=[8 56 96];
• Q1=[1 4 9 10];
• Sys=tf(P1,Q1)
• Roots(P1);
• Roots(Q1);
• pzMAP(sys);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varuncontrolppt-160514063421/85/k12020-control-theory-ppt-9-320.jpg)

![Coding.2
• Num=[49];
• Den=[ 1 4 9 ];
• Sys=tf(num,den);
• load ltiexamples
• ltiview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varuncontrolppt-160514063421/85/k12020-control-theory-ppt-11-320.jpg)

![Coding
• Num=[49 89 96];
• Den=[1 4 9];
• Sys=tf[Num,Den];
• Load ltiexamples
• ltiview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/varuncontrolppt-160514063421/85/k12020-control-theory-ppt-13-320.jpg)

