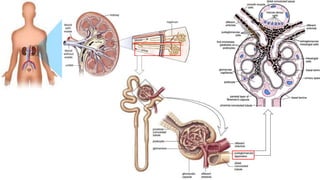
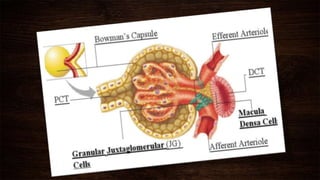
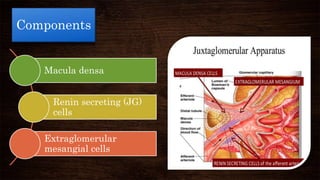
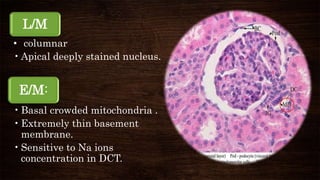
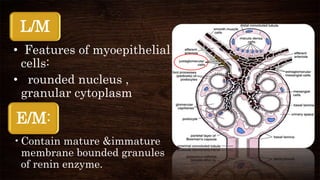
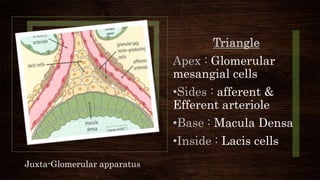
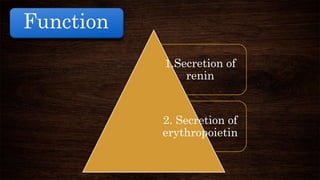
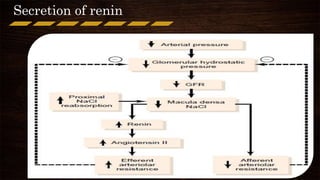
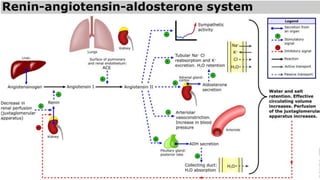
The juxta-glomerular apparatus consists of three main components: the macula densa, renin secreting cells, and extraglomerular mesangial cells. It is located at the junction of the afferent arteriole and distal convoluted tubule of each nephron. The macula densa contains specialized cells that are sensitive to sodium ion concentration in the distal convoluted tubule. The renin secreting cells are modified smooth muscle cells that contain granules of the renin enzyme. The extraglomerular mesangial cells lie in the triangular region between the afferent and efferent arterioles and macula densa. The main functions of the juxt