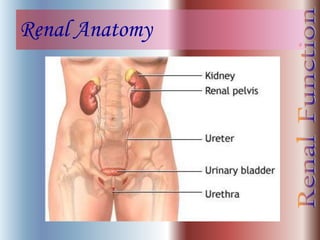
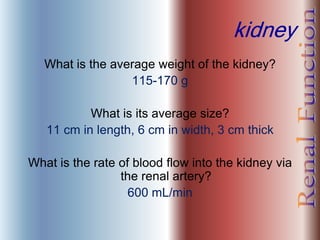
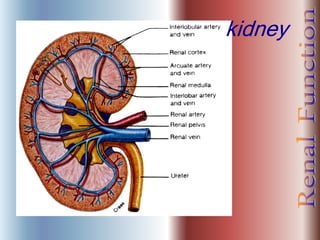
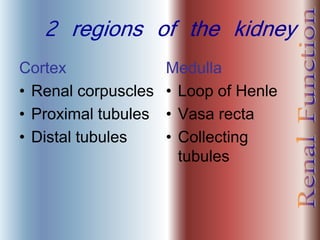
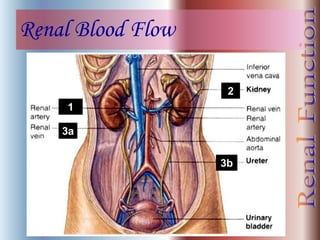
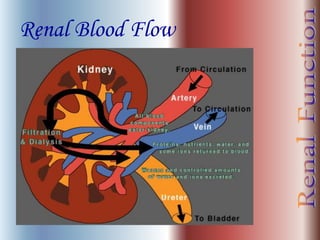
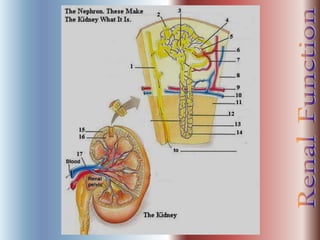
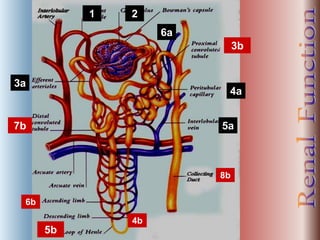
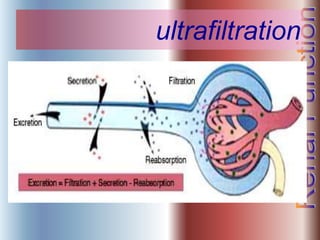
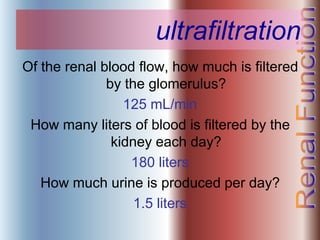
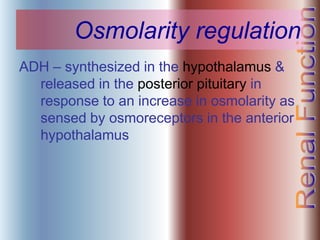
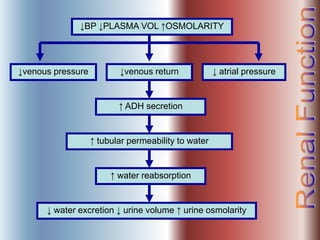
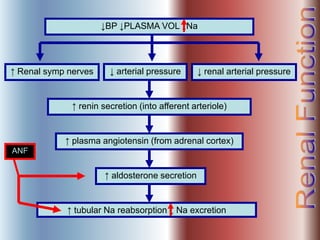
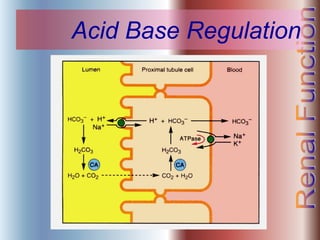
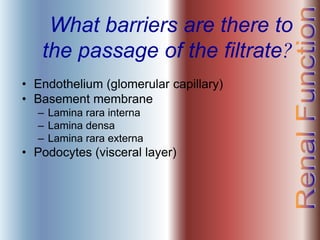
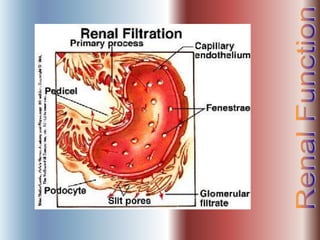
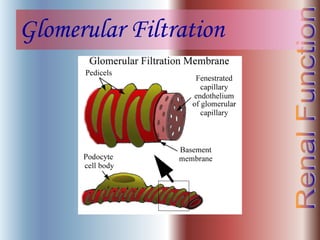
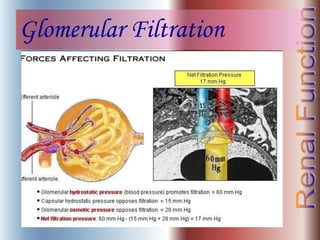
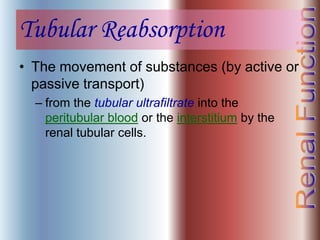
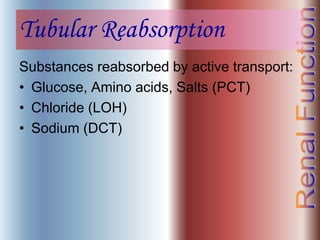
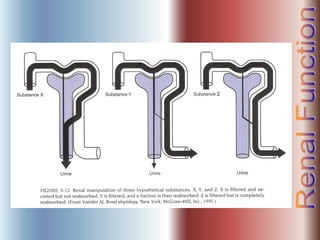
The document discusses renal anatomy, physiology, and urine formation. It describes the two regions of the kidney - the cortex and medulla, and the functional unit of the kidney - the nephron. It explains the three steps in urine formation: glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. Glomerular filtration filters blood in the kidneys and produces an ultrafiltrate. Most of this filtrate is then reabsorbed back into blood in the tubules, while some substances are actively secreted into the tubular fluid for excretion.