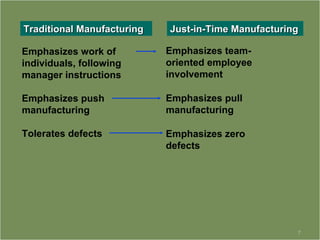
Japanese automakers implemented just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing after WWII to gain more efficient use of limited resources in the face of declining market share. The Toyota Motor Company was the first to fully implement a successful JIT system in the 1970s. JIT aims to produce only what is needed when it is needed and keeps stock levels minimal by having components arrive just before assembly in a close supplier relationship, reducing costs from excess inventory.