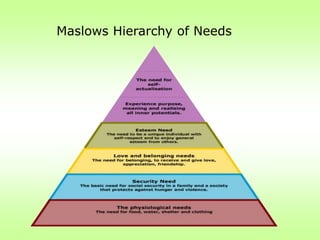
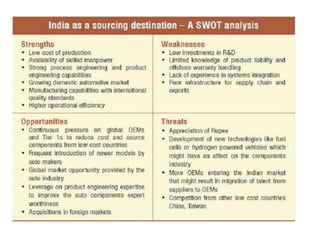
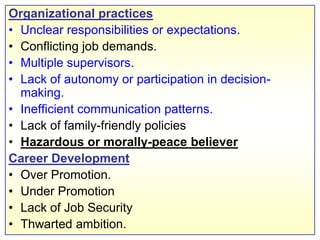
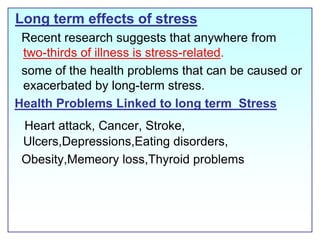
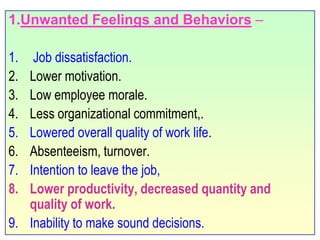
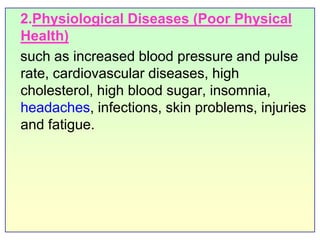
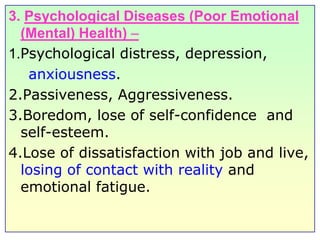
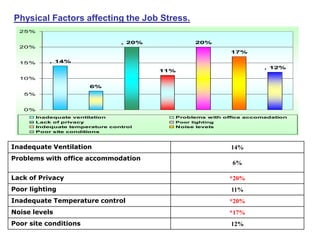
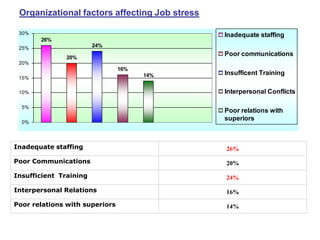
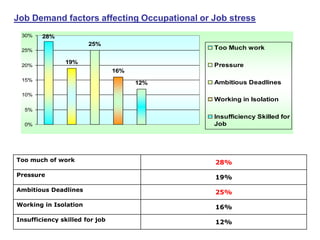
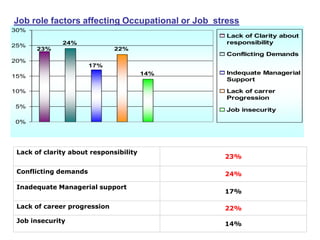
This document discusses job stress and ways to manage it. It begins by outlining various sources of job stress like excessive workload, unclear expectations, and poor workplace relationships. It then describes the physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms of stress as well as its long term health effects. Finally, it provides strategies for reducing stress at both the organizational level, such as ensuring reasonable workloads and defining roles clearly, and individual level, including exercise, relaxation techniques, and changing negative thought patterns.