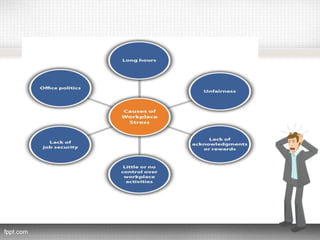
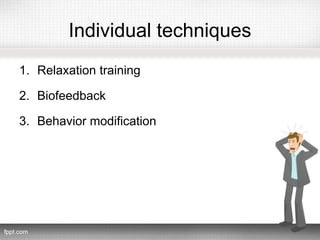
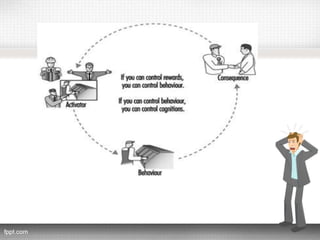
This document discusses stress at work and its causes, effects, and techniques for dealing with it. It begins by defining stress and distinguishing between eustress and distress. It then discusses the physiological, behavioral, and psychological effects of stress at work, including increased heart rate, skin rashes, conflicts, depression, and burnout. Common causes of work stress mentioned include work overload, role ambiguity, and poor working conditions. The document also examines individual differences in vulnerability to stress and covers organizational techniques like emotional climate control and provision of social support, as well as individual techniques such as relaxation training, biofeedback, and behavior modification.