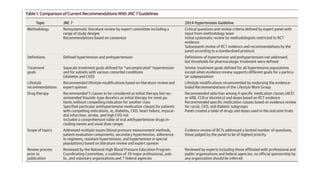
The JNC 8 guideline, established in 2014, provides evidence-based recommendations for managing high blood pressure (BP) in adults, emphasizing randomized controlled trials. It focuses on three key questions regarding the initiation of pharmacologic therapy, BP goal achievement, and differences between antihypertensive drug classes, resulting in nine graded recommendations based on the strength of the evidence. The guidelines include specific BP treatment thresholds for different population age groups and suggest initial treatment options based on demographic factors, such as race and comorbid conditions.