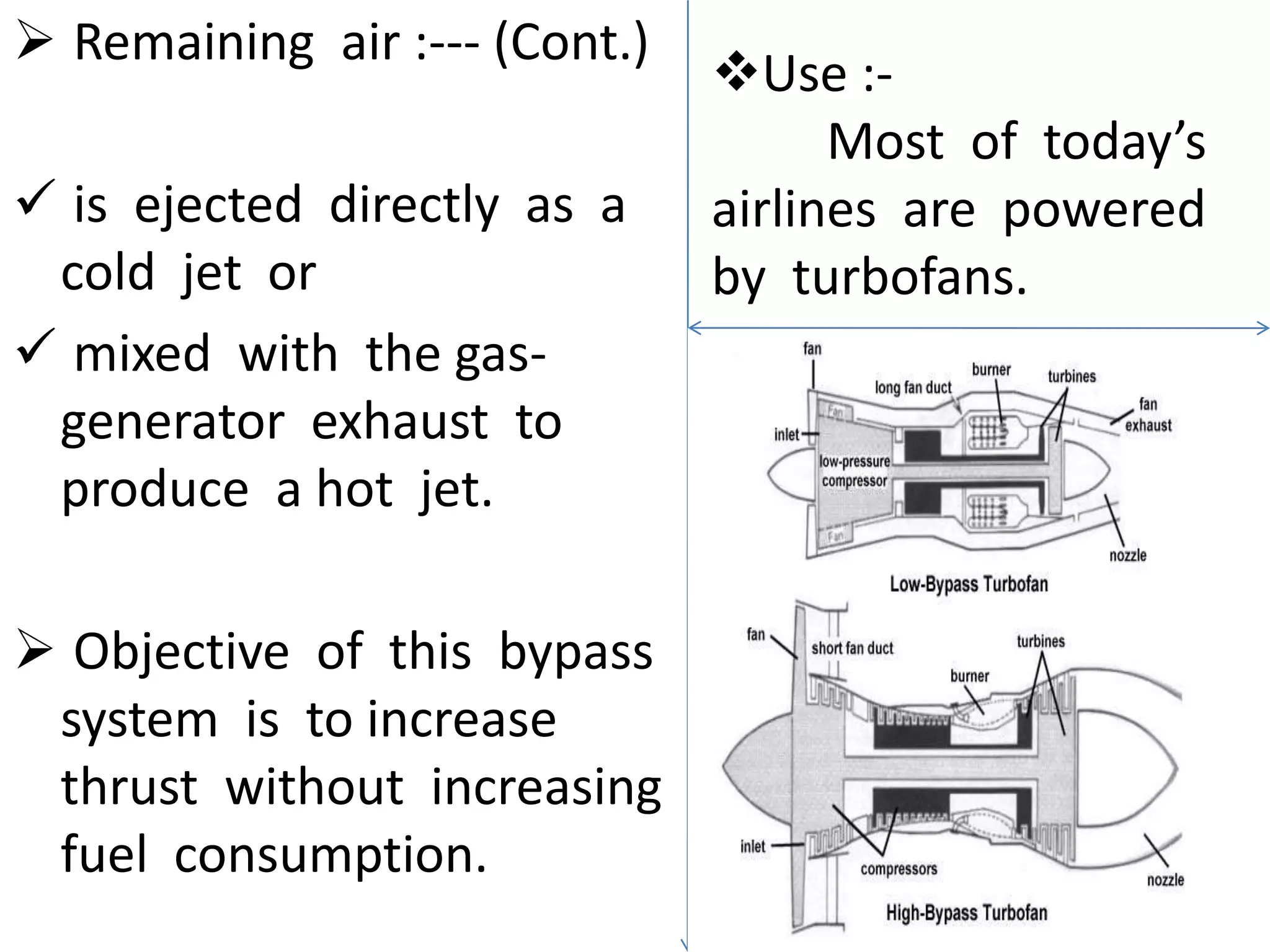
Jet engines work by taking in air and accelerating it rearward through a nozzle, generating thrust according to Newton's Third Law. The jet engine was developed in the early 20th century by Hans von Ohain and Frank Whittle. Modern jet engines come in several types but generally work by compressing air, mixing it with fuel, combusting the mixture, and expelling the hot gases through a turbine to produce thrust. Jet engines are primarily used to power aircraft but also have applications in boats and other vehicles.