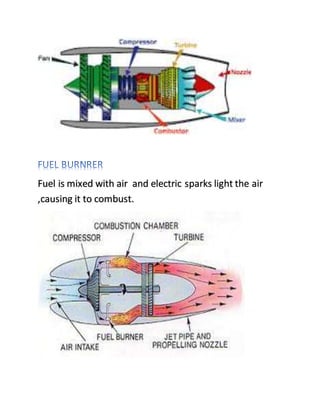
1. A jet engine works by sucking in air at the front, compressing it, mixing it with fuel and igniting it, and then blasting the expanding hot gases out of the back through a nozzle to produce thrust.
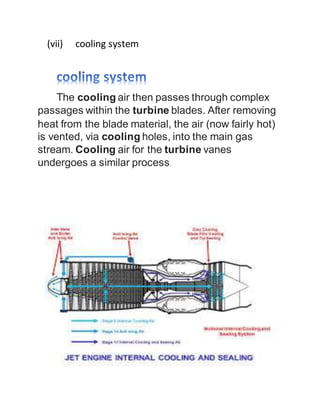
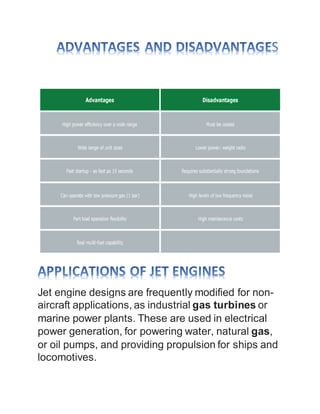
2. Key components of a jet engine include compressors, combustion chambers, turbines, and exhaust nozzles. The compressed air is mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber. The expanding hot gases then power the turbines before exiting through the nozzle.
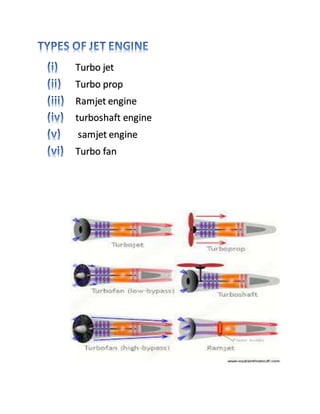
3. Jet engines come in different types including turbojet, turboprop, ramjet, and turbofan engines which vary in their design and use of compressor and turbine components but all work on the basic principle of producing thrust