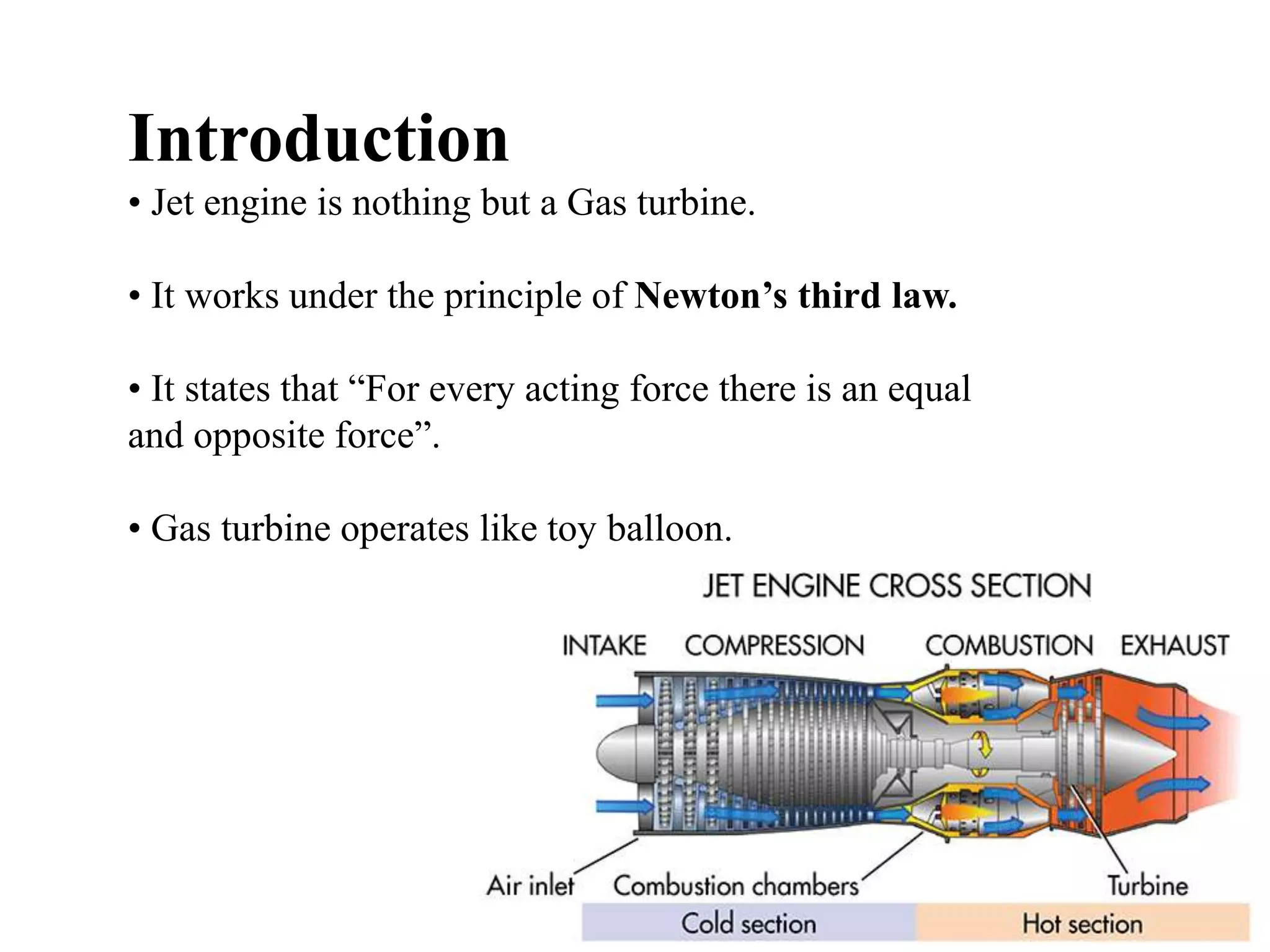
The document discusses jet propulsion and jet engines. It provides a brief history of jet engines, noting the first jet engine was built by Egyptian scientists in 100 BC. It then describes the major components of a jet engine, including the fan, compressor, combustor, turbine, mixer, and nozzle. The document explains how a jet engine works, from air intake into the compressor to combustion and exhaust through the turbine and nozzle. It also outlines different types of jet engines, such as ramjet, turbojet, turbofan, turboprop, and turboshaft, providing some key details about each.