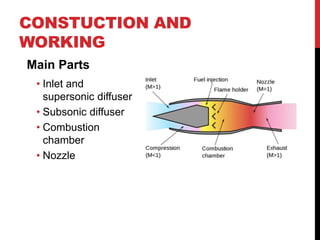
This document discusses different types of jet engines. It begins by explaining that a jet engine works on Newton's third law of motion and operates similarly to a toy balloon. It then provides a brief history, noting the first jet engine was invented in ancient Egypt. The main parts of a jet engine are described as the air intake, compressor, fuel burner, combustion chamber, turbine, and jet pipe/nozzle. Several types of jet engines are then outlined in more detail, including turbojets, turbofans, turboprops, ramjets, and pulse jets. Their key components and applications are summarized. The document concludes by comparing advantages and disadvantages of jet engines relative to internal combustion engines.