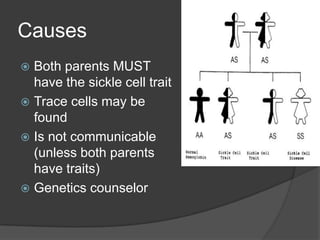
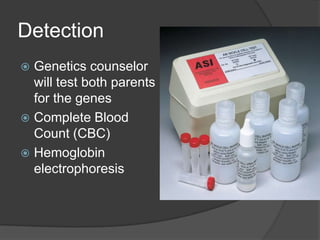
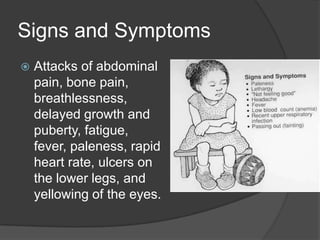
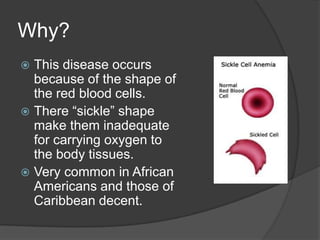
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder caused when both parents carry the sickle cell trait and pass it to their child. The red blood cells take on a sickle shape, which prevents them from properly carrying oxygen throughout the body. Symptoms may appear after four months of age and include attacks of pain, breathing issues, fatigue and more. While there is no cure, new treatments are helping those with sickle cell anemia live longer, into their 50s rather than the previous average of 20-40 years of age. Prevention includes vaccinations, genetic counseling before having children, and living a normal life with proper precautions.