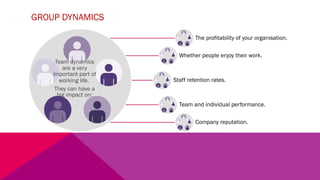
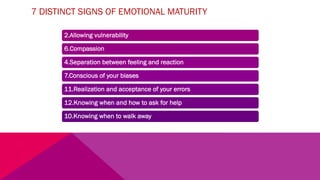
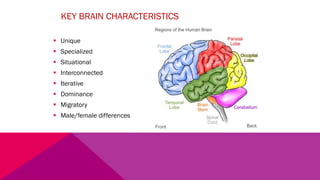
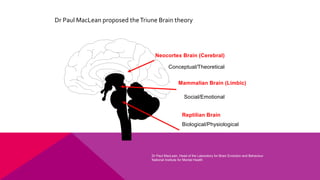
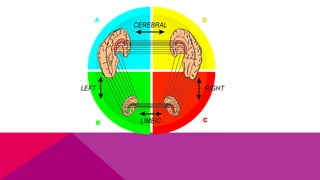
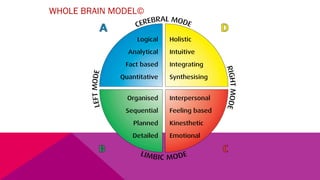
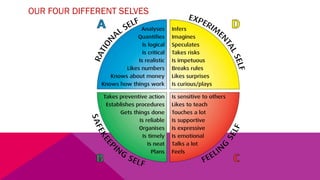
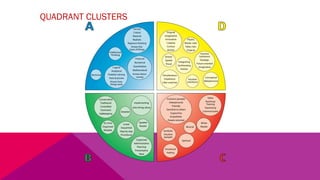
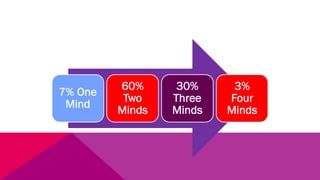
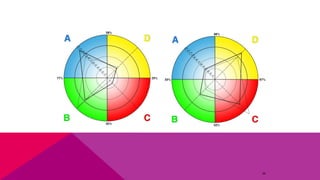
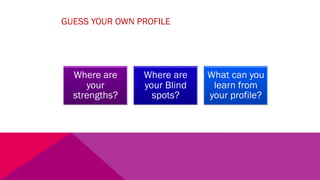
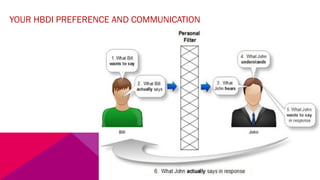
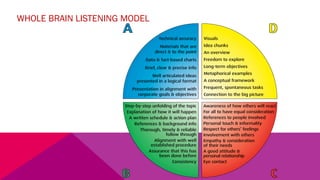
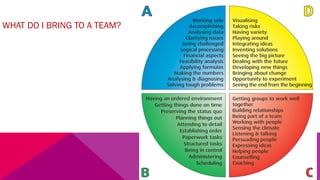
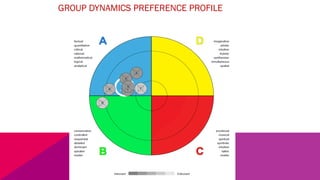
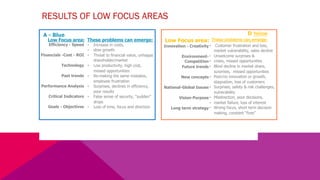
The document discusses the importance of emotional intelligence in enhancing individual and collective leadership capabilities, team dynamics, and workplace relationships. It outlines various aspects of emotional maturity, decision-making, and problem-solving, emphasizing the role of neuroscience in understanding behavior. Additionally, it identifies common challenges that arise from low focus areas within organizations and the need for collaborative communication to overcome them.