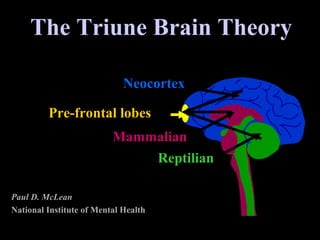
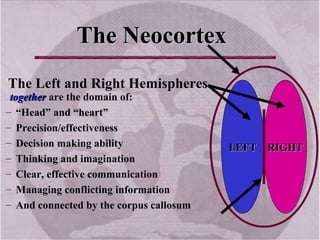
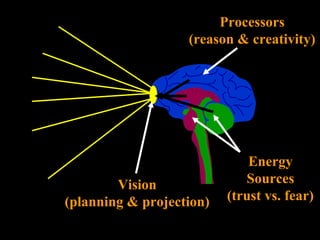
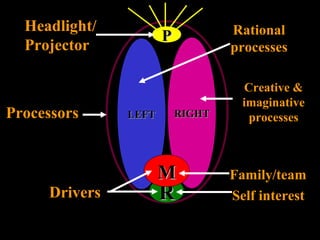
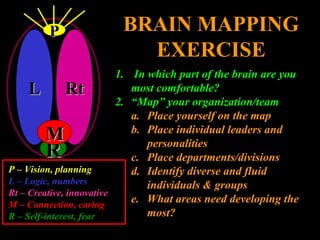
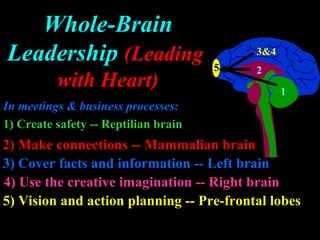
The document discusses how leading with vision and positive emotional leadership can inspire loyalty and commitment. It explores different leadership styles and their emotional impacts, finding that styles with positive emotion resulted in better financial returns. The document then discusses theories of the triune brain and its reptilian, mammalian and neocortical parts, and how leading with both head and heart by addressing the needs of each brain region can create more effective whole-brain leadership.