This document provides an overview of emotional intelligence. It discusses the history and definitions of emotional intelligence. Key aspects that were summarized include:
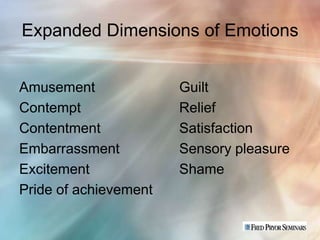
1. Emotional intelligence involves the capacity for recognizing our own feelings and those of others, motivating ourselves, and managing emotions well.
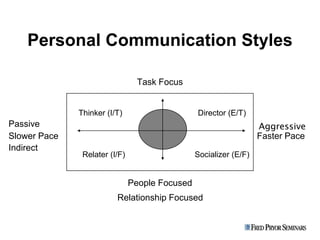
2. There are four main components of emotional intelligence: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management.
3. Effective leadership requires skills like empathy, adaptability, and persuasiveness that are aspects of emotional intelligence. Developing self-awareness, self-confidence, and trust are important for leaders.