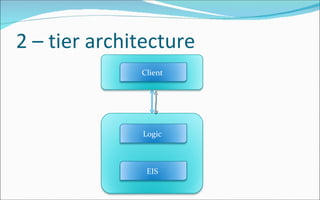
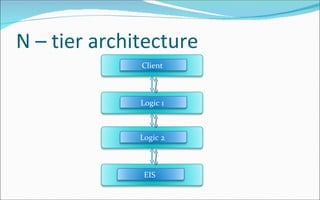
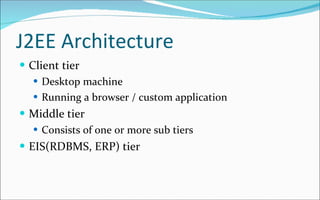
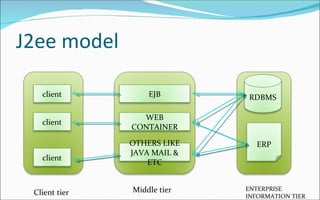
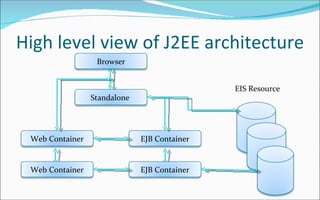
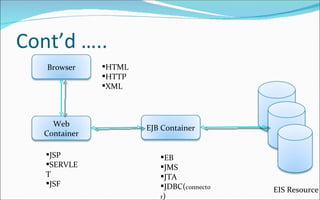
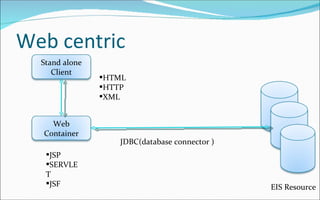
The document discusses the evolution of distributed computing and challenges in developing enterprise applications across multiple machines, noting how Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) platform addresses these issues through its support for multi-tier architectures. It describes the J2EE architecture and programming model which promotes component-oriented code reuse, leverages inter-tier communication, and focuses on integration across tiers through technologies like Java servlets, JavaServer Pages, Enterprise JavaBeans and more. Key aspects of the model-view-controller (MVC) architecture are also outlined.