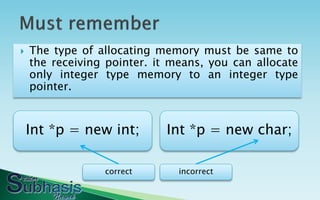
The document explains dynamic memory allocation in C++, detailing how to allocate and deallocate memory using 'new' and 'delete' operators. It provides syntax examples for creating object pointers and emphasizes the importance of matching data types between the allocated memory and the pointer. Additionally, it discusses the use of 'const' in pointer types, illustrating how it impacts the mutability of the pointer and the value it references.