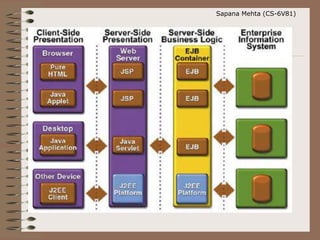
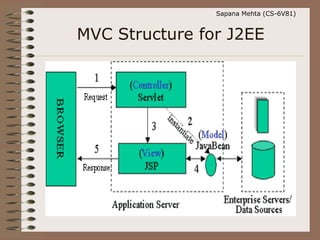
The document discusses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern. It explains that MVC separates an application into three main components: the Model, the View, and the Controller. The Model manages the data logic, the View displays the presentation logic, and the Controller handles user input and interaction between the Model and View. Some key benefits of MVC include flexibility to change views without affecting other components, and separating concerns for improved maintenance and testing.