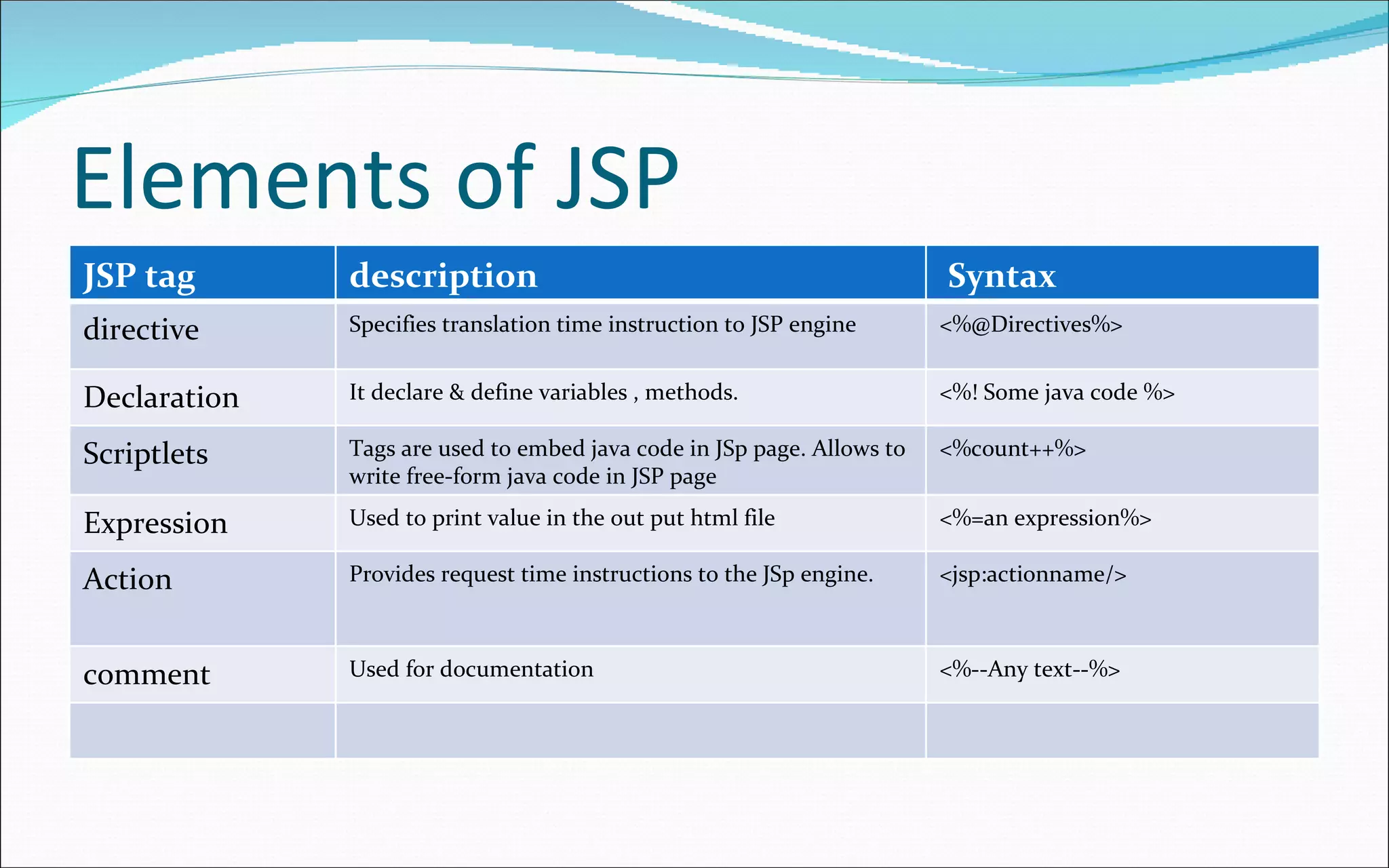
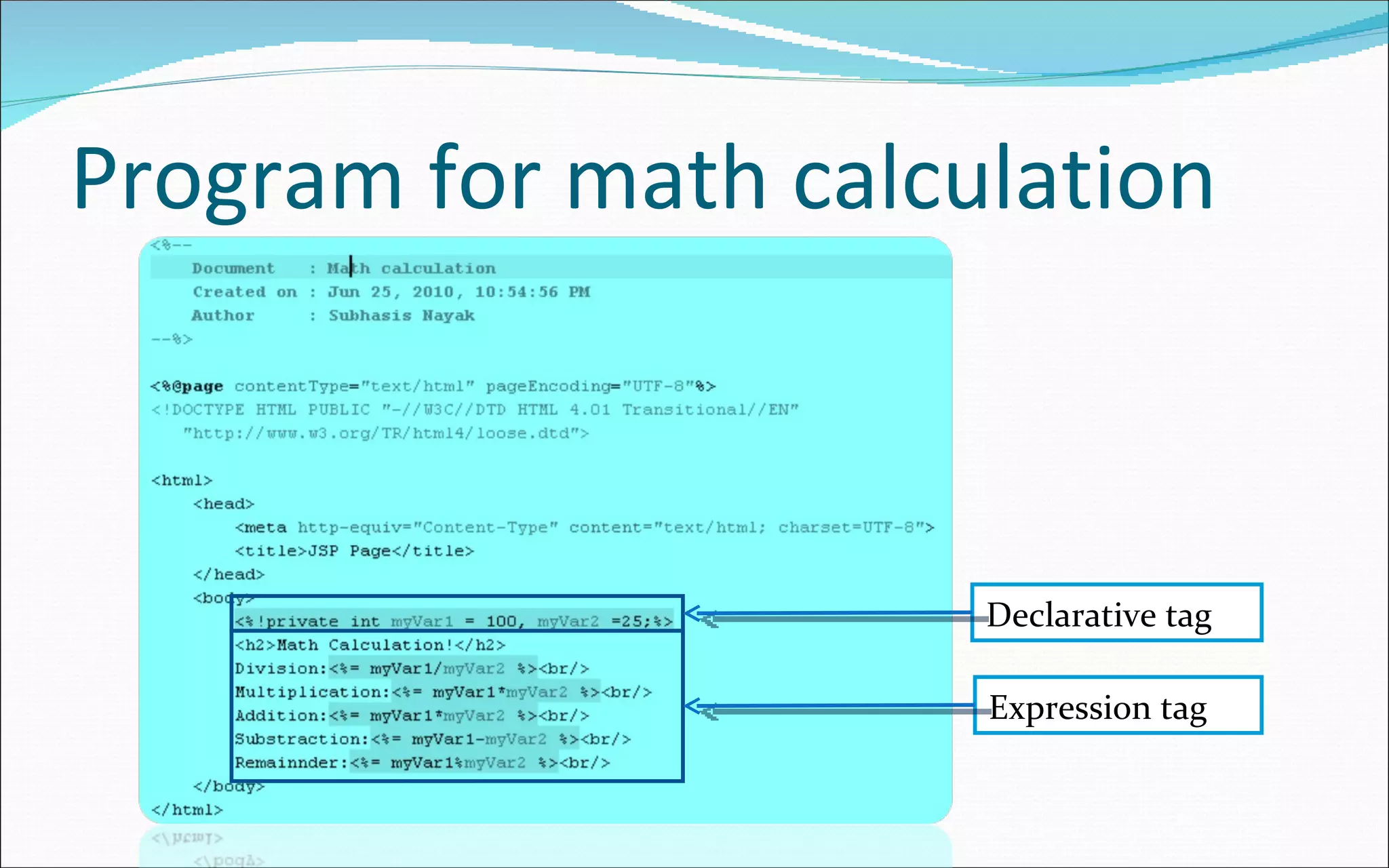
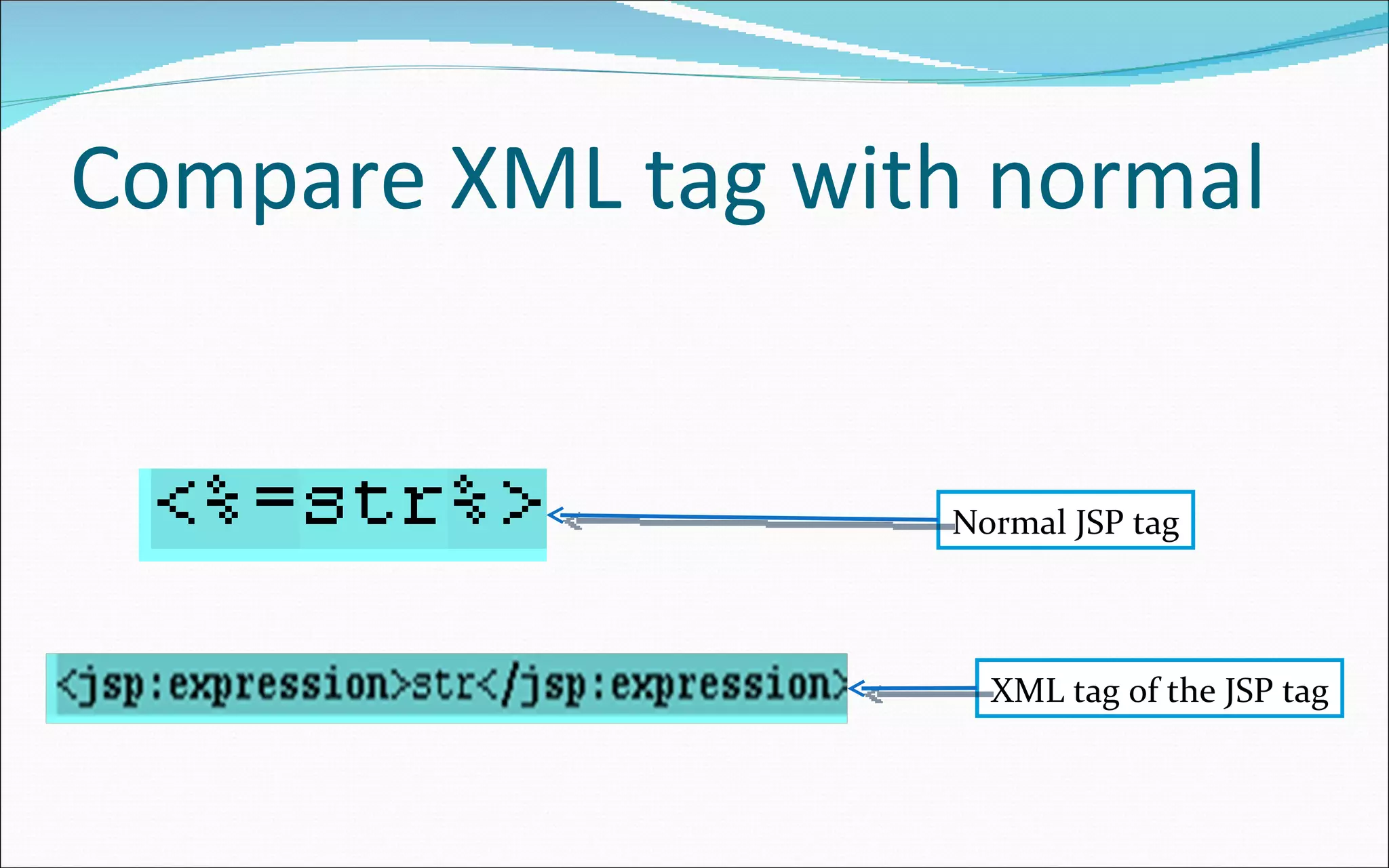
The document provides information about Java Server Pages (JSP) including what JSP is, its features, life cycle, advantages, architecture models, elements like tags, directives, comments, and examples of simple JSP pages and code. Key points covered include:
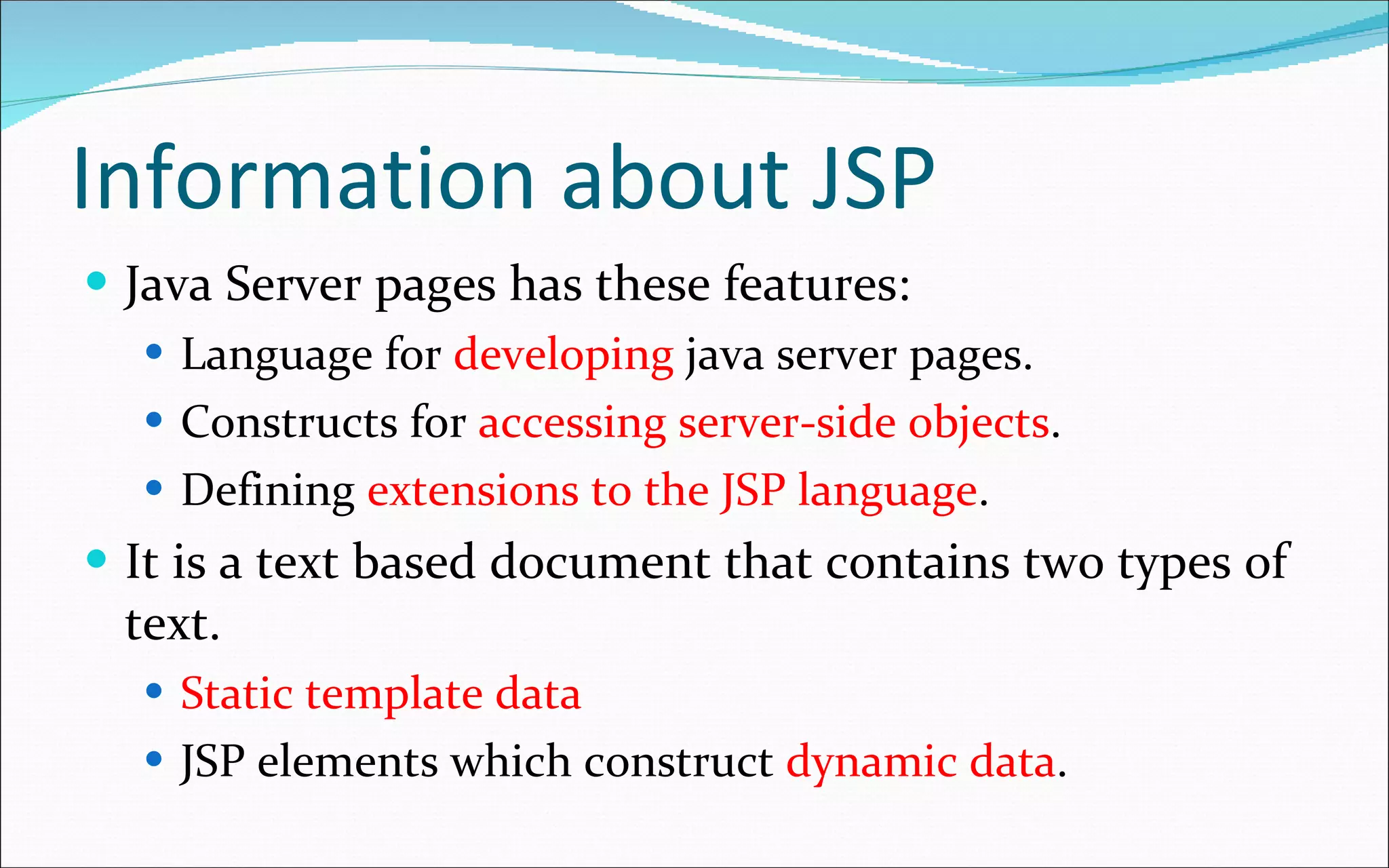
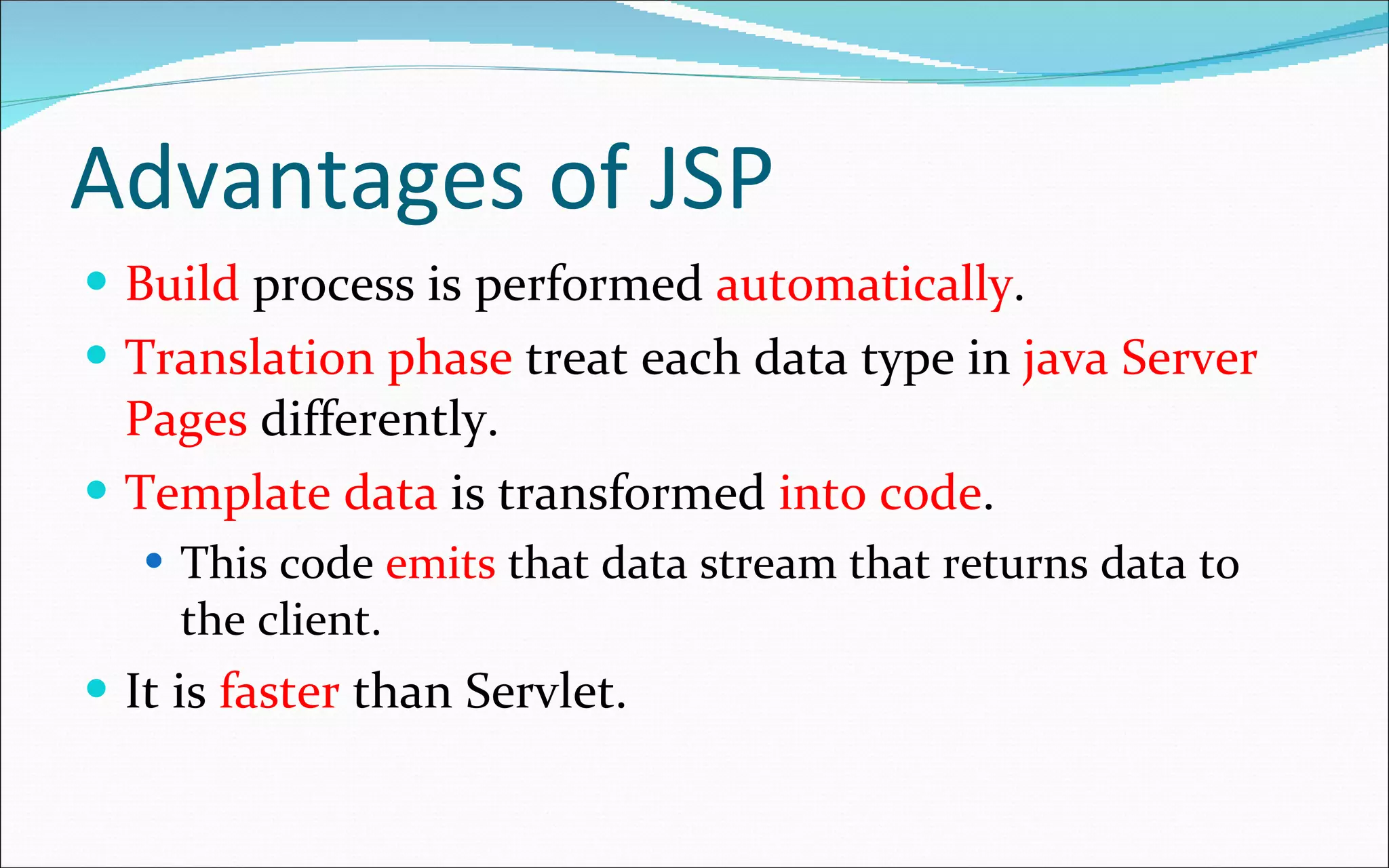
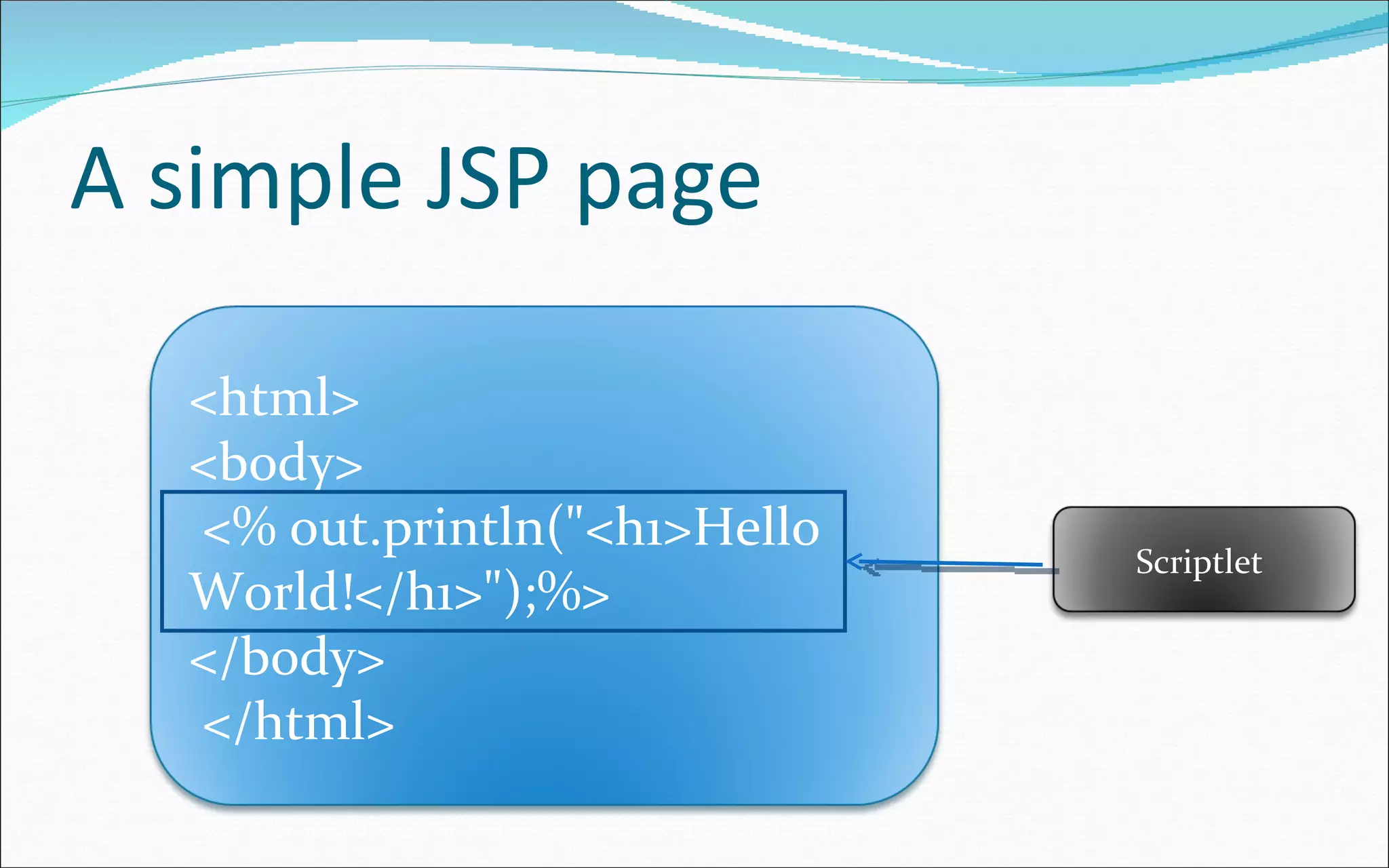
- JSP is a text-based document that contains static and dynamic content and describes how to create a response from a request.
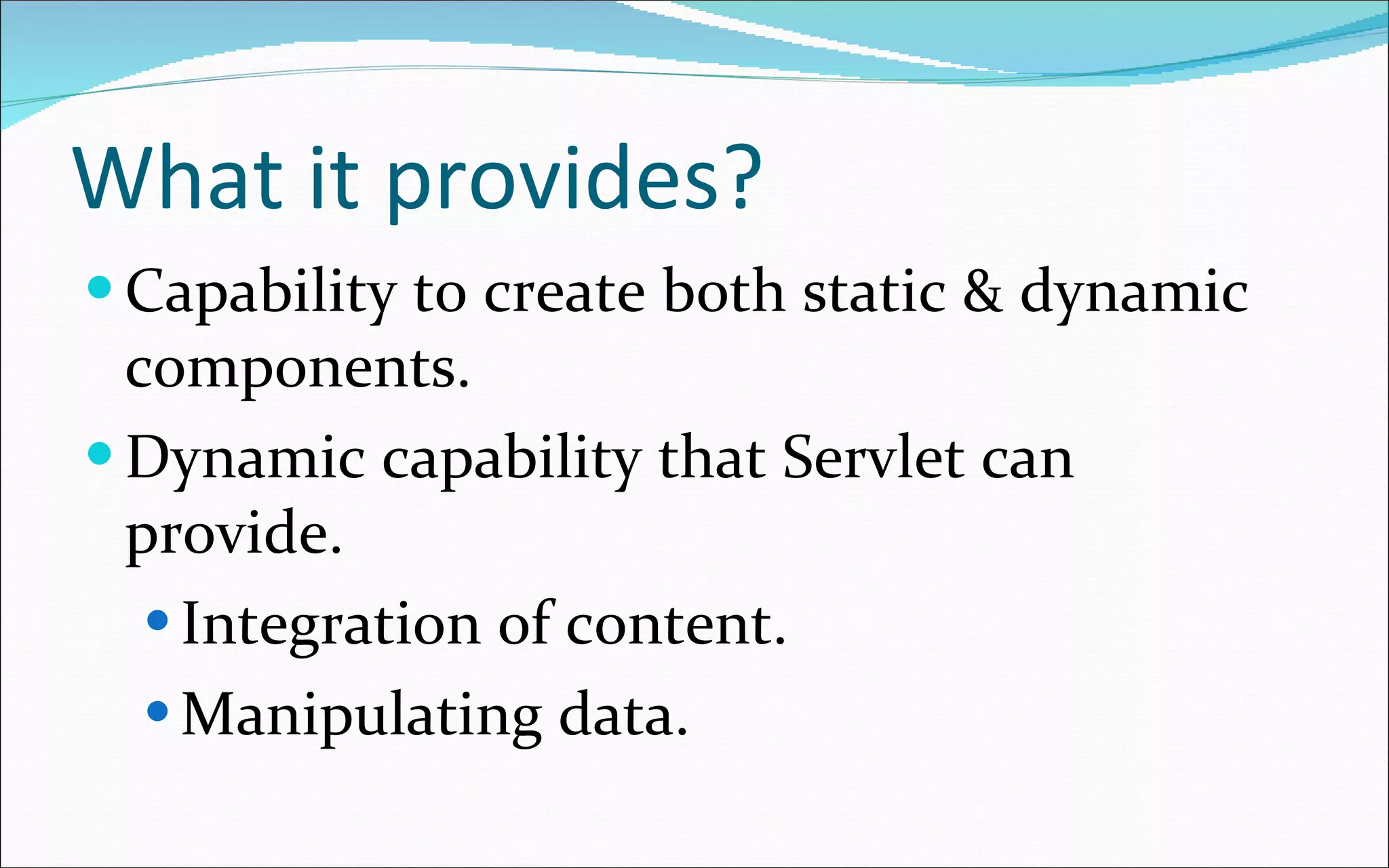
- It provides capabilities for both static and dynamic components, content manipulation, and integration.
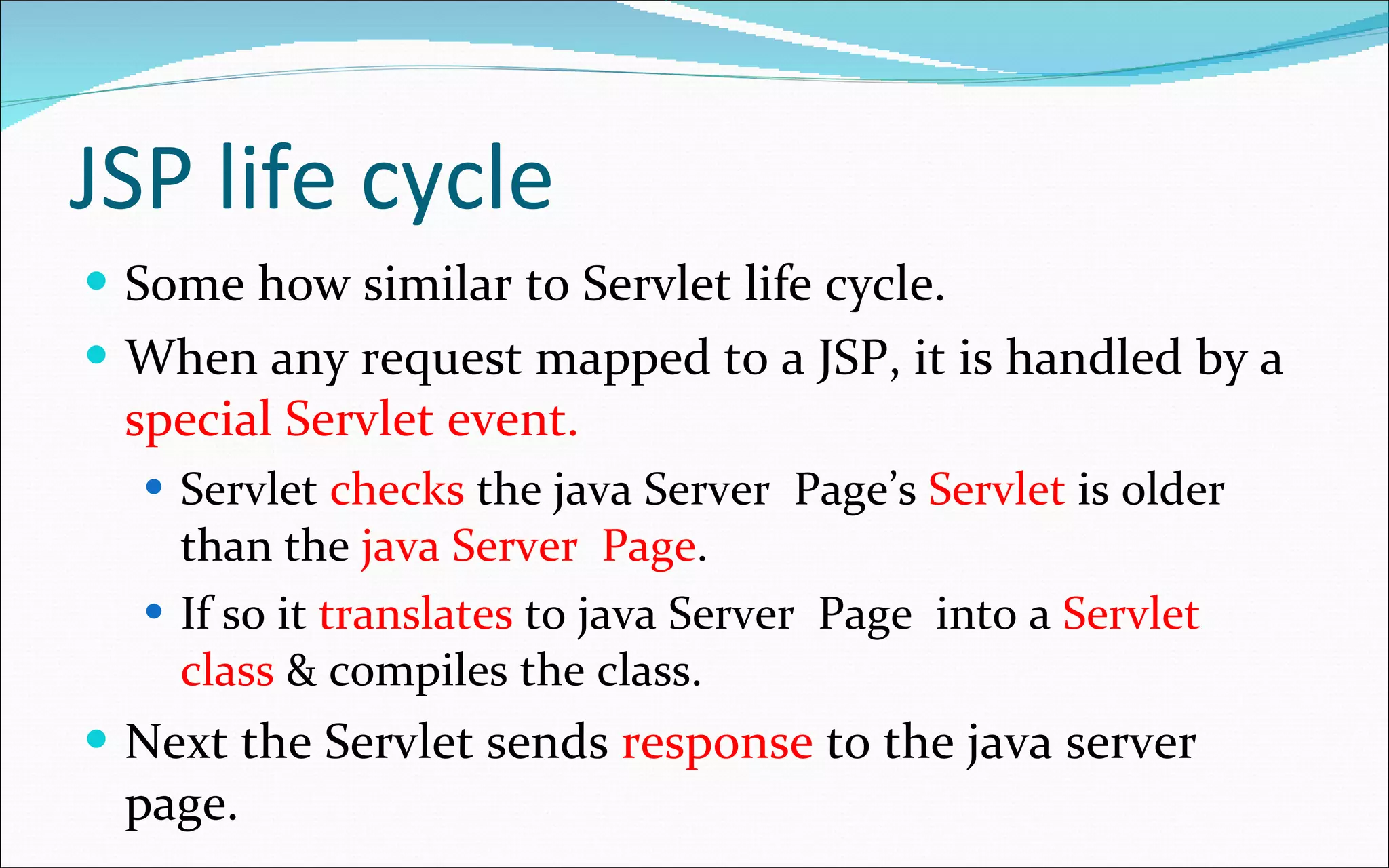
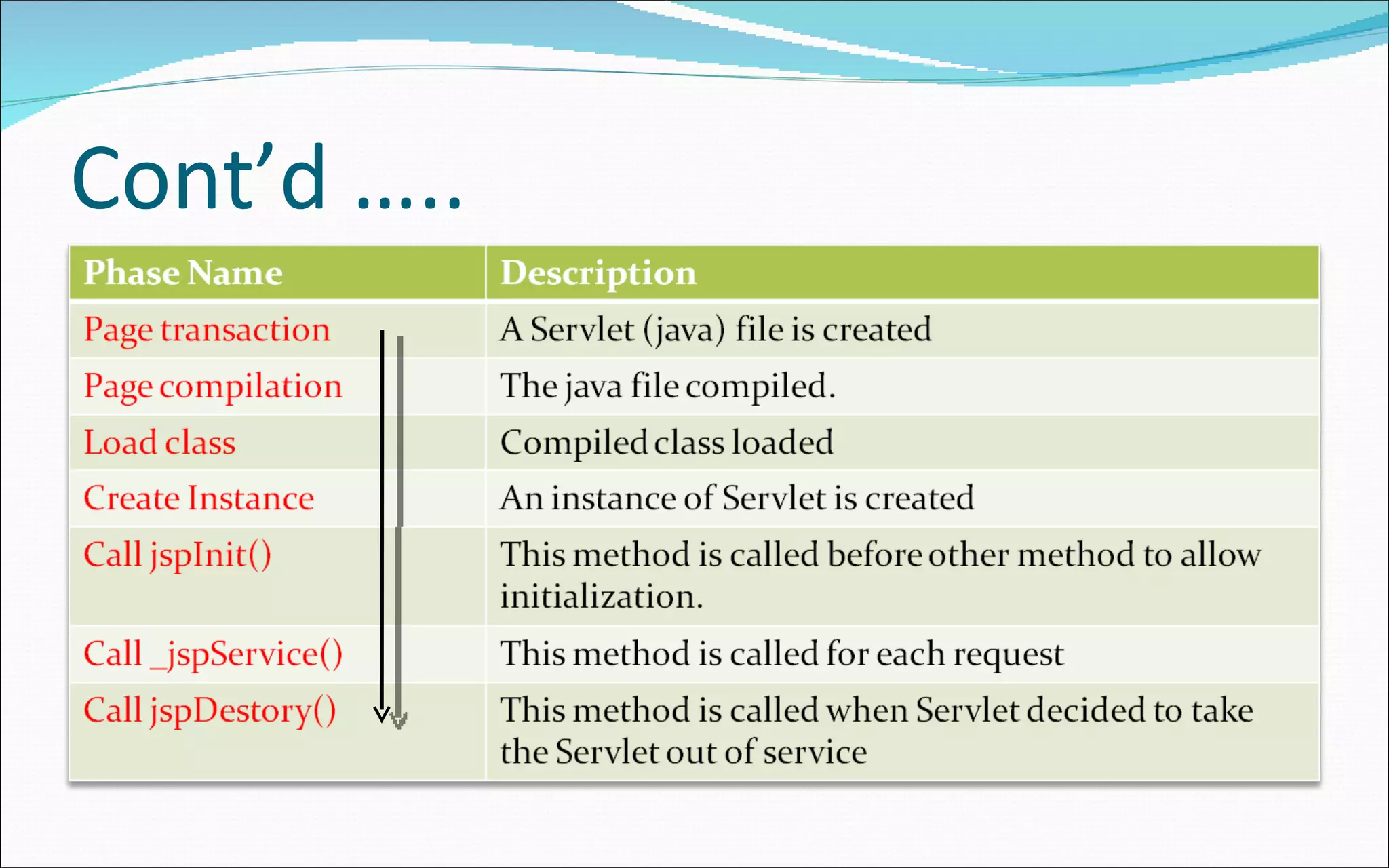
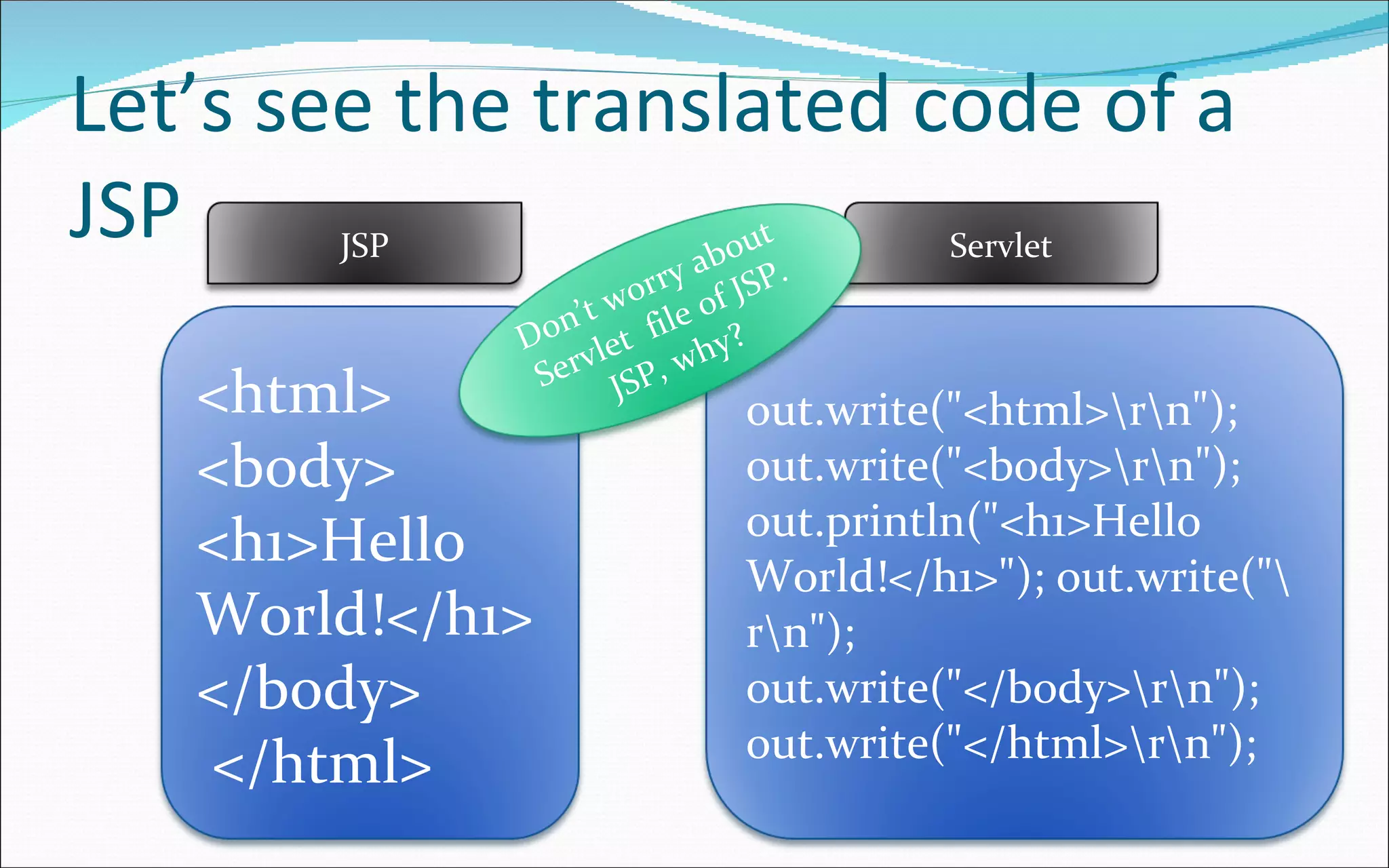
- The JSP life cycle involves translation to a servlet class if newer than the existing one, then compiling and executing the response.
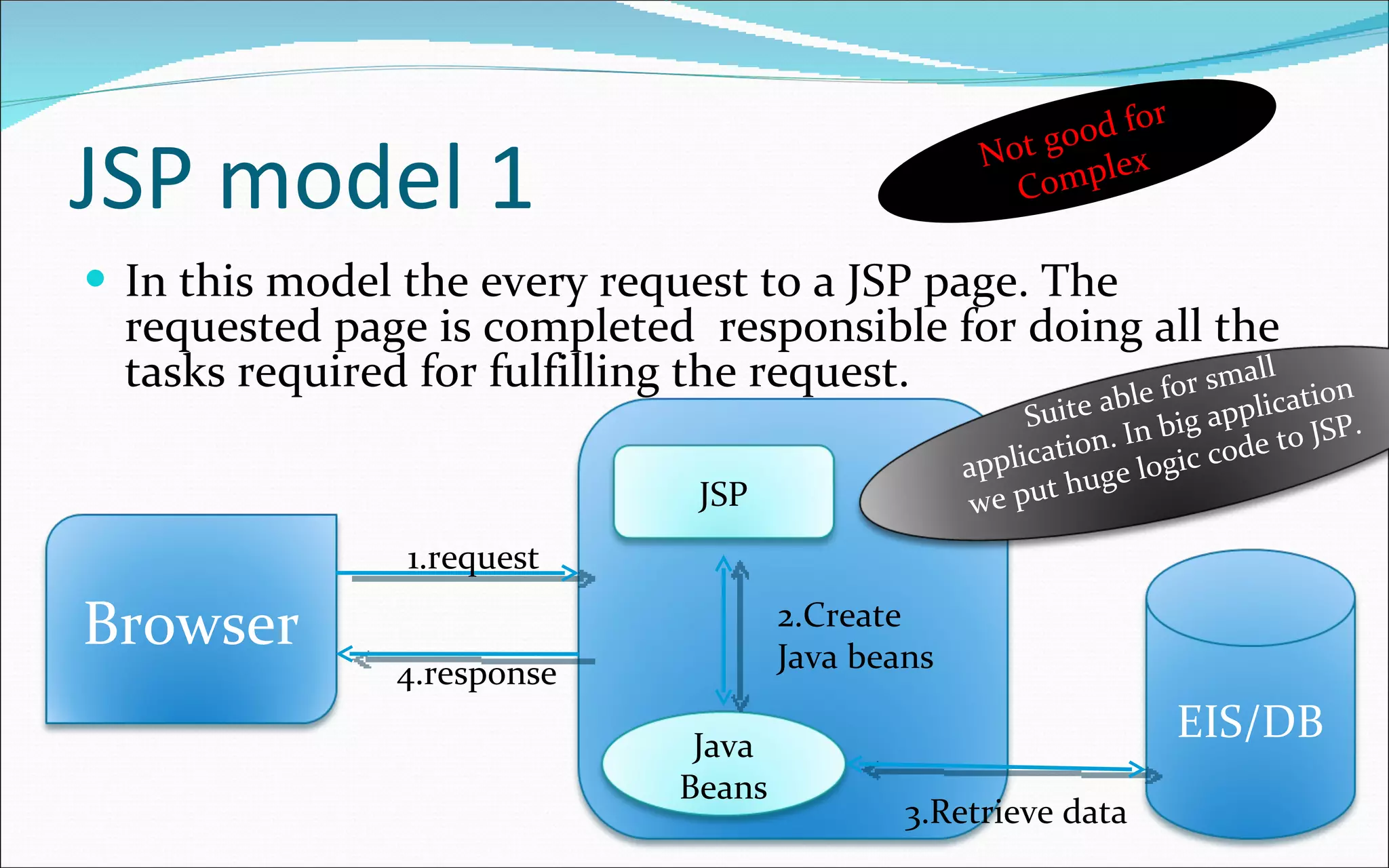
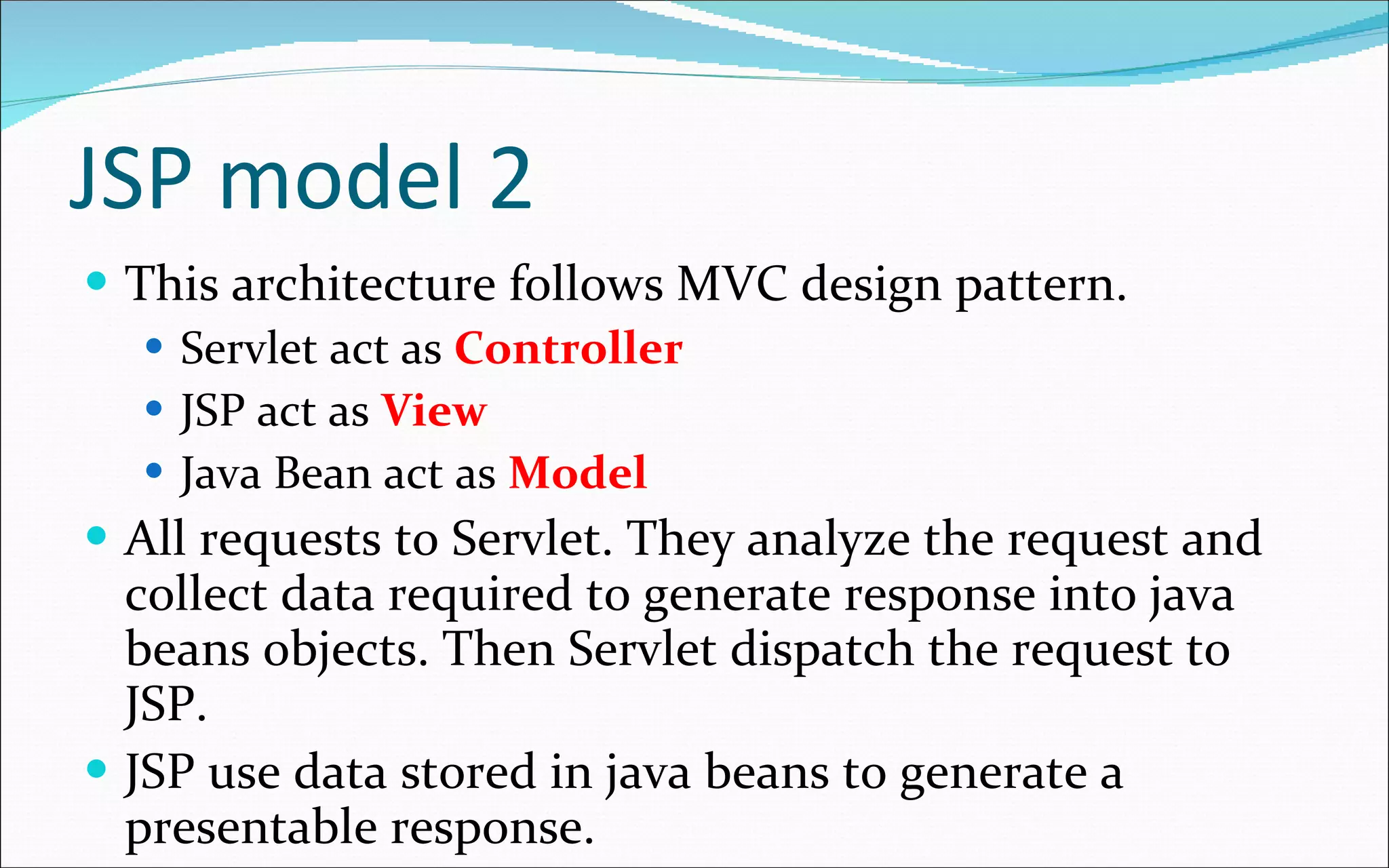
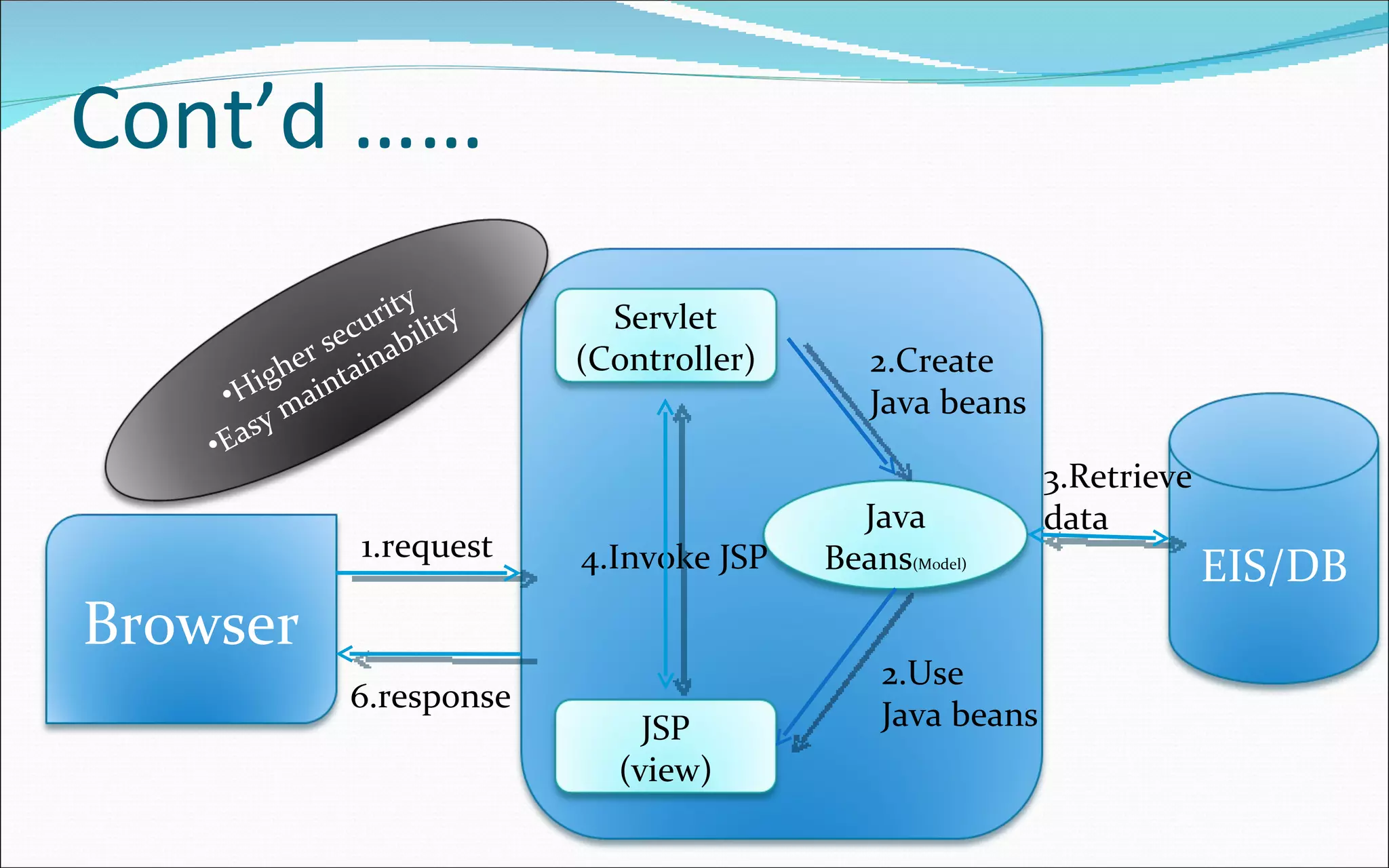
- There are two main architectural models: model 1 where each JSP handles a