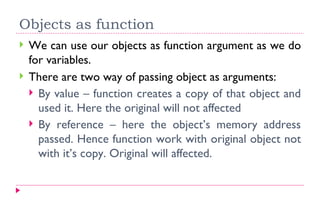
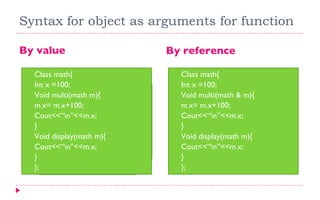
Objects are created from classes but do not allocate separate memory for methods. An array of objects allows multiple instances of a class to be stored. Objects can be passed as arguments to functions by value, where a copy is used, or by reference, where the original object is modified.


![Let’s define a class & create it’s object Defining class Creating object class student { int id; char name[25]; }; student stu1,stu2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objects2-100629061212-phpapp01/85/how-to-create-object-3-320.jpg)

![Array of objects An array having class type elements known as array of objects. We can create an array which each block will hold an object . The objects must be of a single class. Why? class student { int id; char name[25]; }; student stu[6];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objects2-100629061212-phpapp01/85/how-to-create-object-5-320.jpg)