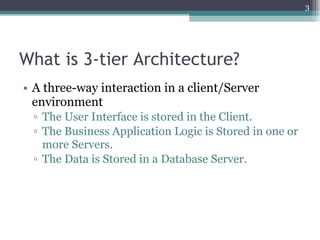
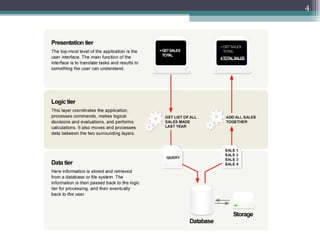
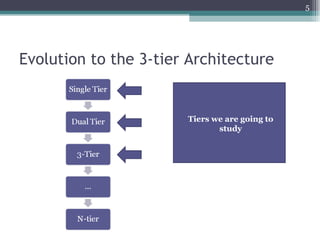
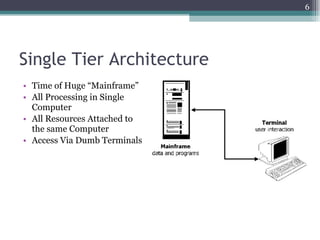
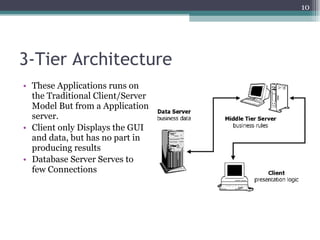
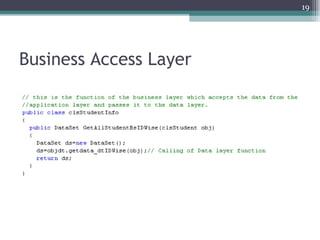
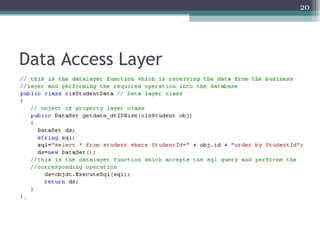
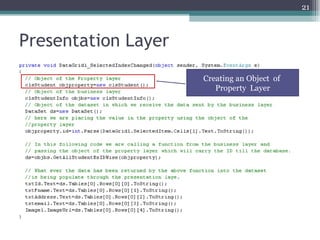
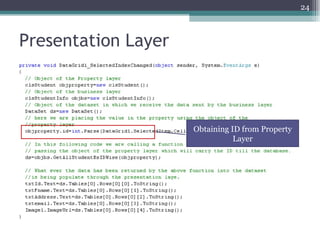
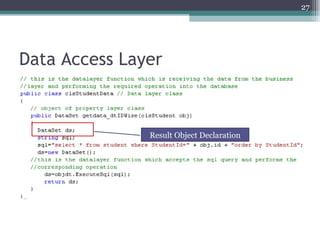
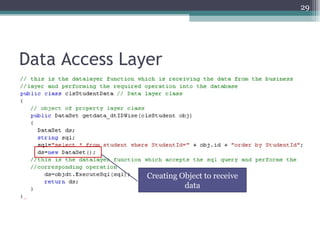
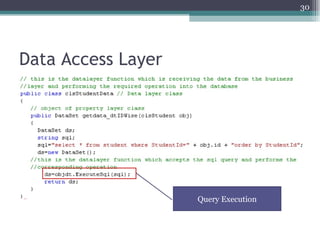
The document discusses 3-tier architecture, which separates an application into three logical layers - the presentation layer, business logic layer, and data layer. It describes how this architecture evolved from earlier single-tier and dual-tier models. The 3-tier model provides advantages like scalability, reusability, security, and availability. While more complex than 2-tier, it allows for improved performance in medium to large systems by distributing the application across servers. An example is provided of implementing a 3-tier application using ASP.NET with distinct presentation, business, and data access layers.