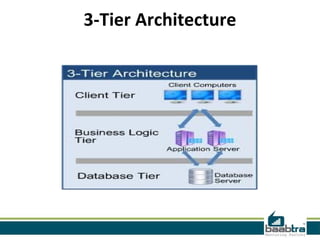
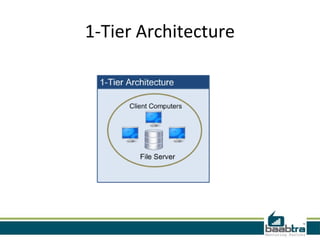
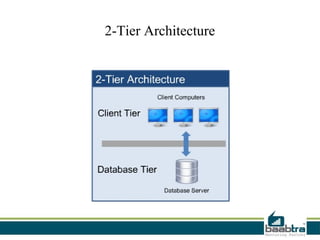
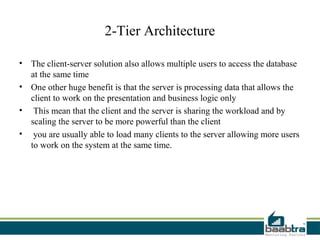
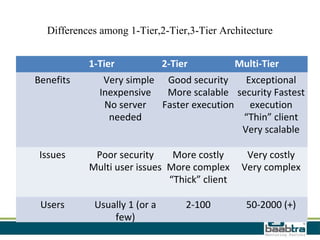
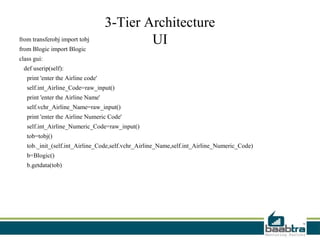
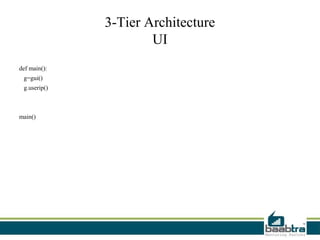
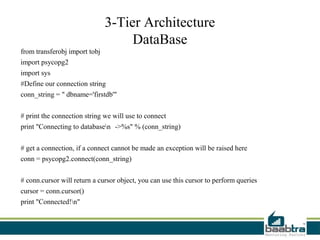
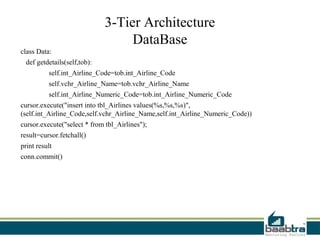
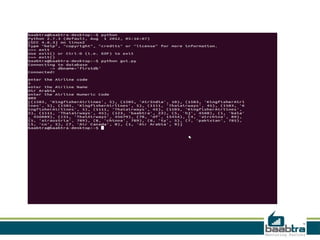
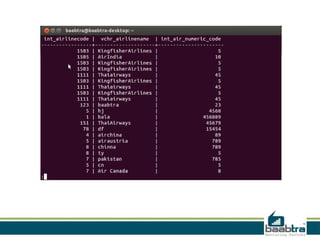
This document discusses 1-tier, 2-tier, and 3-tier architectures. The 1-tier architecture has all components in one layer, making it simple but insecure. The 2-tier client-server architecture separates the client and database server for better security. The 3-tier architecture introduces a middle layer to move business logic away from the client, improving scalability and security while making the client thinner. Benefits and issues of each architecture are compared, with 3-tier seen as most scalable and secure though also most complex and costly. Sample code demonstrates how the 3 layers of presentation, business logic, and data would communicate in a 3-tier architecture.