This document provides an introduction to Java Server Pages (JSP) including what JSP is, its features, life cycle, advantages, architecture models, elements, processing, and tags. Key points include:
- JSP is a text-based document that describes how to create a response object from a request object for a given protocol. It allows both static and dynamic content.
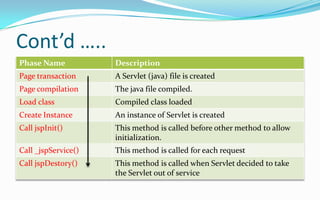
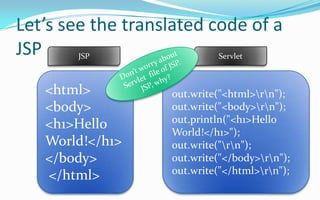
- The JSP life cycle involves translation of the JSP file into a servlet class which is then compiled and executed in response to requests.
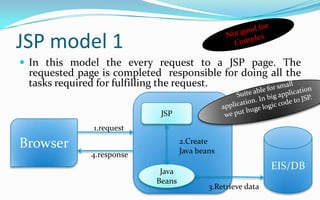
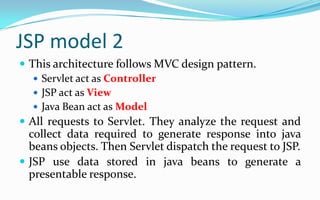
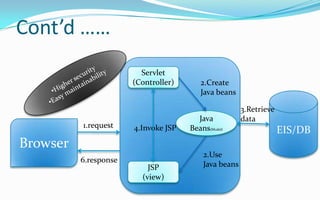
- The two main JSP architecture models are model 1 where all logic is in the JSP, and model 2 which follows an MVC pattern with separation of controller, view and