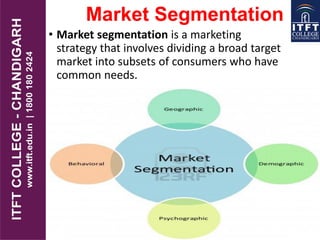
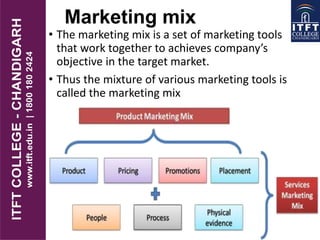
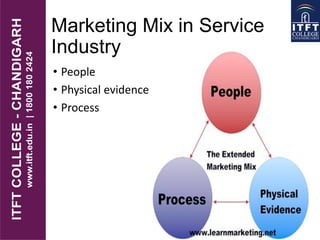
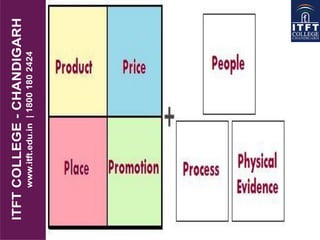
The document outlines the concept of market segmentation in tourism marketing, emphasizing the importance of dividing a broad market into smaller segments based on shared characteristics. It discusses various bases for segmentation, including geography, psychography, demography, and behavioral responses, and highlights the significance of creating a tailored marketing mix for each segment. Additionally, it explains the marketing mix components, particularly in the service industry, focusing on product, price, promotion, place, people, process, and physical evidence.