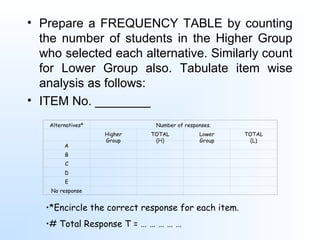
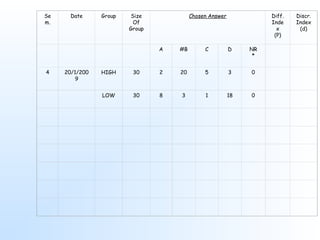
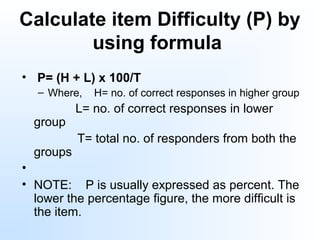
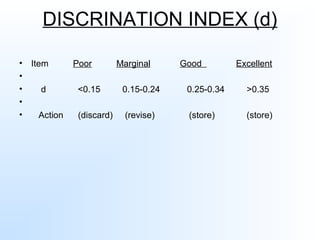
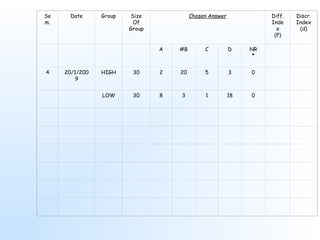
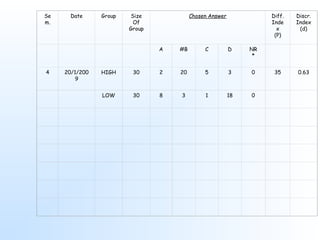
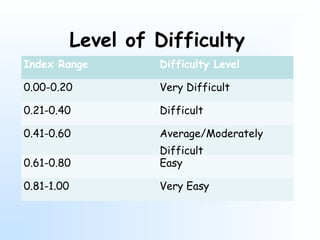
This document discusses item analysis, which is the process of evaluating the effectiveness of individual multiple choice questions (MCQs) on a test. Item analysis has several objectives, including selecting appropriate questions, determining question difficulty, and ensuring questions can differentiate between more and less capable test takers. It involves arranging test scores and separating respondents into high- and low-scoring groups. Key metrics calculated through item analysis are the difficulty index, which indicates how hard a question is, and the discrimination index, which shows how well a question distinguishes between strong and weak test takers. Item analysis provides useful information for improving test questions and guiding students.