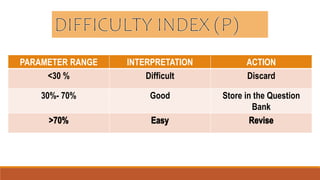
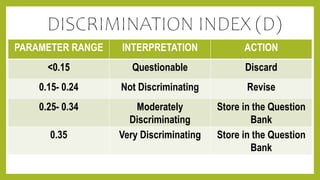
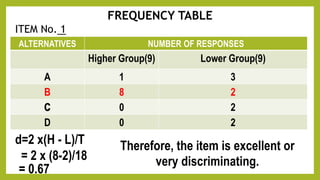
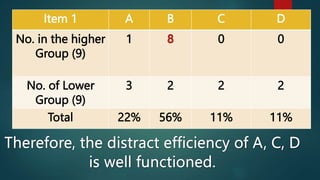
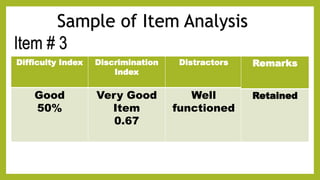
This document discusses item analysis, which is a process that examines student responses to test questions to evaluate the quality of those questions and the test overall. Item analysis provides statistical information about whether questions were easy or difficult for students, how well questions discriminated between higher- and lower-performing students, and whether questions measured what they intended to measure. It can help identify common student misconceptions and guide future test preparation. Key aspects of item analysis include calculating the difficulty index, discrimination index, and analyzing how well distractors functioned on multiple choice questions. The information provided by item analysis helps improve the quality and validity of assessment items and tests.