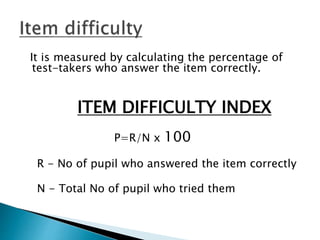
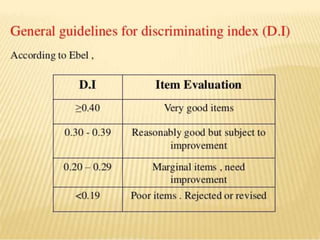
The document discusses item analysis, a method used to evaluate test items for effectiveness in measuring the same construct and discriminating among students' abilities. Key concepts include calculating difficulty and discrimination indices, assessing item performance, and making revisions to improve test quality. The analysis aids educators in understanding student performance, enhancing test construction skills, and refining teaching strategies.