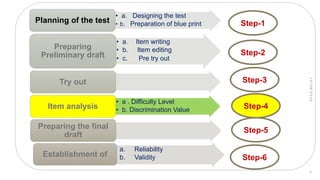
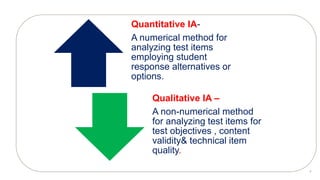
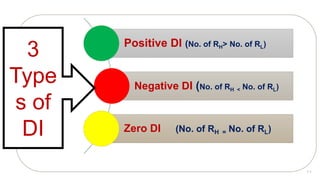
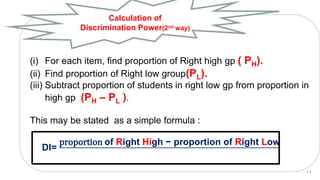
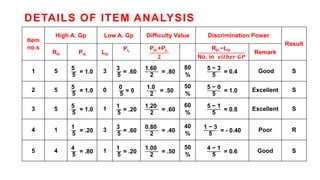
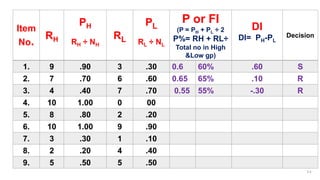
The document provides details about conducting an item analysis of a test. It discusses the key steps in item analysis which include: 1) arranging student answer sheets in order of performance and dividing them into high and low groups, 2) calculating the difficulty level and discrimination power of each item, and 3) using the results to select items to keep, modify, or eliminate from the test. The item analysis helps evaluate the quality of individual test items and identify areas for improving the test and future item writing.