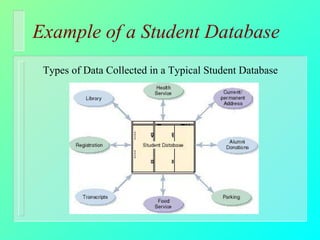
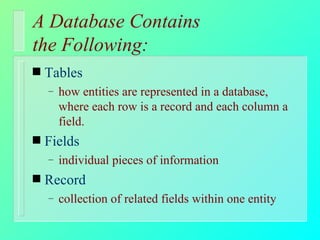
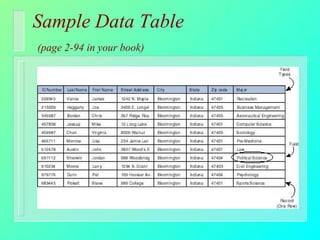
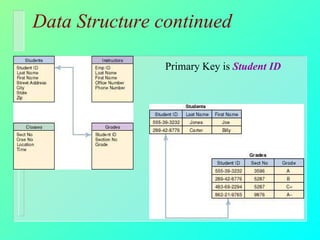
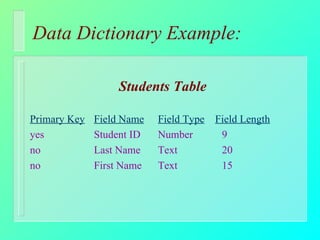
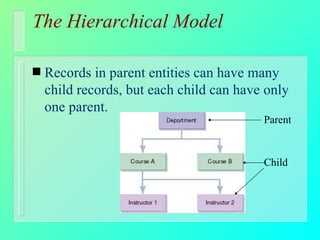
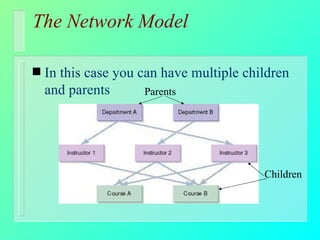
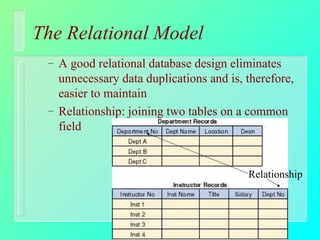
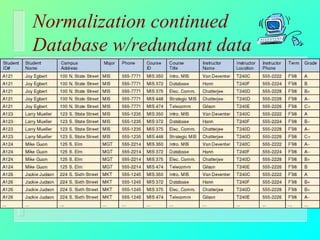
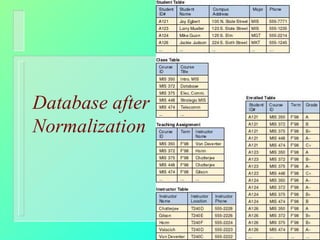
Databases have become important for organizing data in modern organizations. A database contains tables with records and fields to store related data. Database management systems allow users to create, access, and modify this data. Emerging trends include client/server systems that split databases onto servers and client computers, object-oriented databases that treat database components as reusable objects, data mining that analyzes stored data to understand customers and business, and linking web applications to organizational databases.