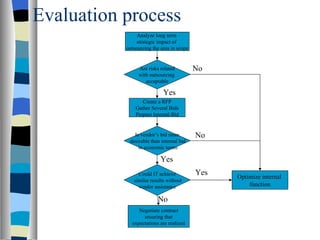
The document proposes a methodology for evaluating whether to outsource functions or keep them in-house. If outsourcing, the methodology helps select a vendor and develop contracts to ensure promised results. Reasons for outsourcing include improving efficiency, acquiring new resources, following trends, reducing uncertainty, eliminating troublesome functions, and enhancing credibility. However, outsourcing also carries risks that must be carefully considered in the evaluation process.