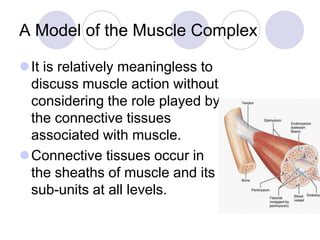
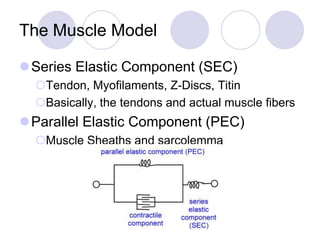
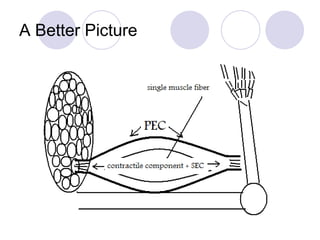
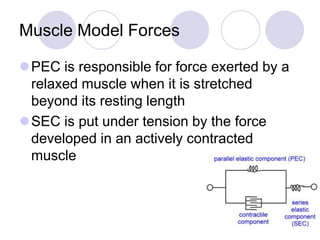
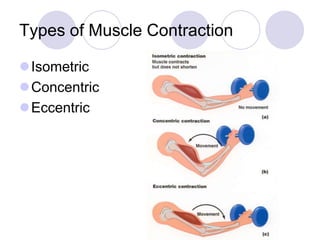
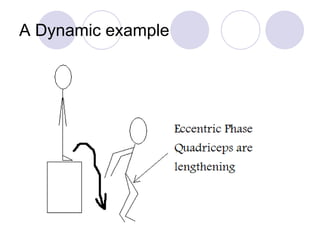
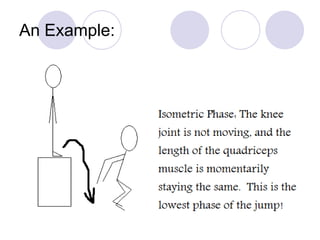
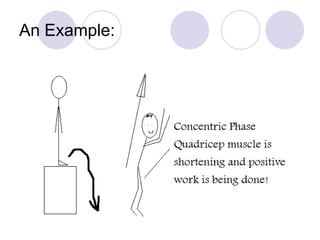
This document discusses the muscular system and strength training. It explains that muscles work with connective tissues like tendons, and describes the series elastic component (SEC) and parallel elastic component (PEC) of the muscle model. The document also discusses the different types of muscle contractions (isometric, concentric, eccentric), muscle actions like agonist and antagonist muscles, and the importance of the nervous system in strength and muscle development. Functional strength training aims to improve abilities like speed and endurance, while structural training focuses more on muscle hypertrophy.