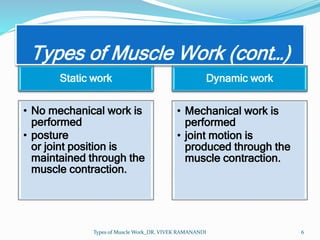
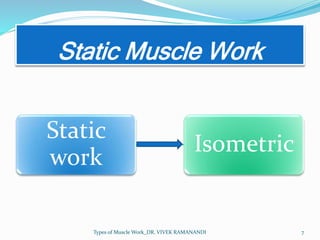
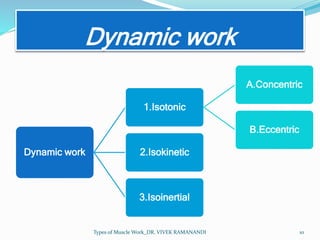
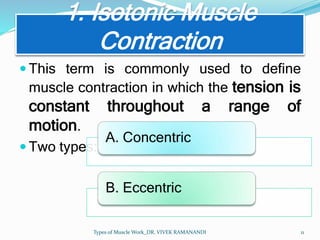
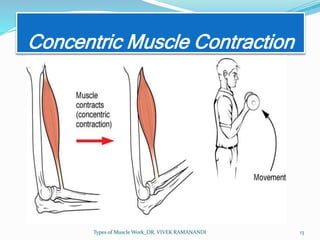
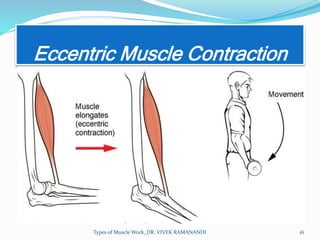
The document defines and describes different types of muscle work. Static work involves maintaining posture or joint position through muscle contraction without mechanical work, while dynamic work produces mechanical work and joint motion. Static work includes isometric contractions that generate force without changing muscle length. Dynamic work includes isotonic contractions where tension is constant during motion, as well as isokinetic and isoinertial contractions where velocity or resistance remains constant during motion.