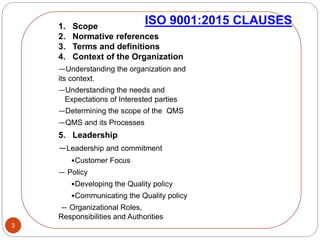
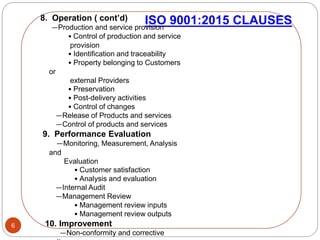
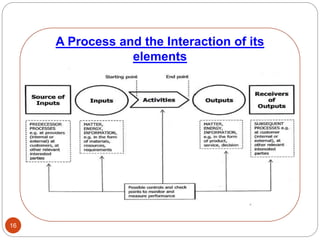
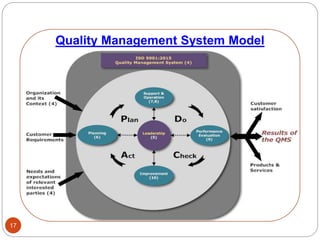
The document outlines the key clauses of the ISO 9001:2015 quality management standard. It discusses the standard's scope and references in clauses 1-3. Clause 4 covers understanding the organization's context and interested parties. Clause 5 addresses leadership and management commitment. Clause 6 discusses quality planning. Clause 7 covers resource management and documentation. Clause 8 focuses on operational planning, design, and control of outputs. Clause 9 is about performance evaluation through monitoring, measurement, and management review. Finally, clause 10 covers improvement through nonconformity handling and continual improvement.