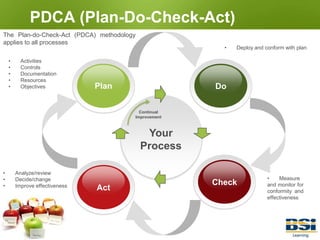
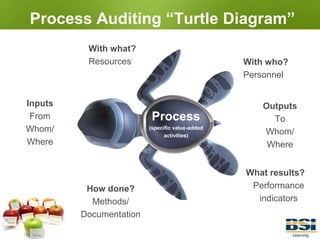
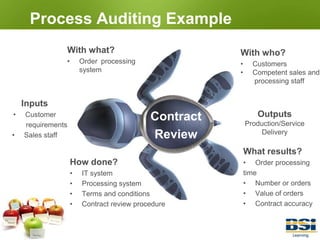
The document provides information on conducting internal audits, including:
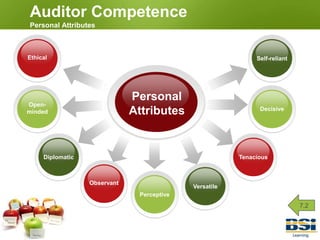
1) It discusses auditor competence and responsibilities, such as being objective, ethical, and maintaining confidentiality.
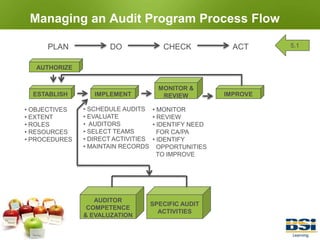
2) It explains how to manage an audit program, including establishing objectives and procedures, scheduling audits, and maintaining records.
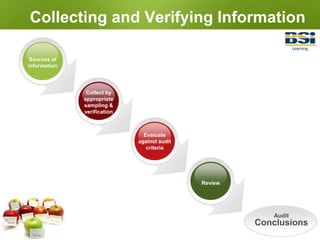
3) It describes the audit process, from planning and document review, to conducting on-site activities like interviews and observations, and preparing the audit report.