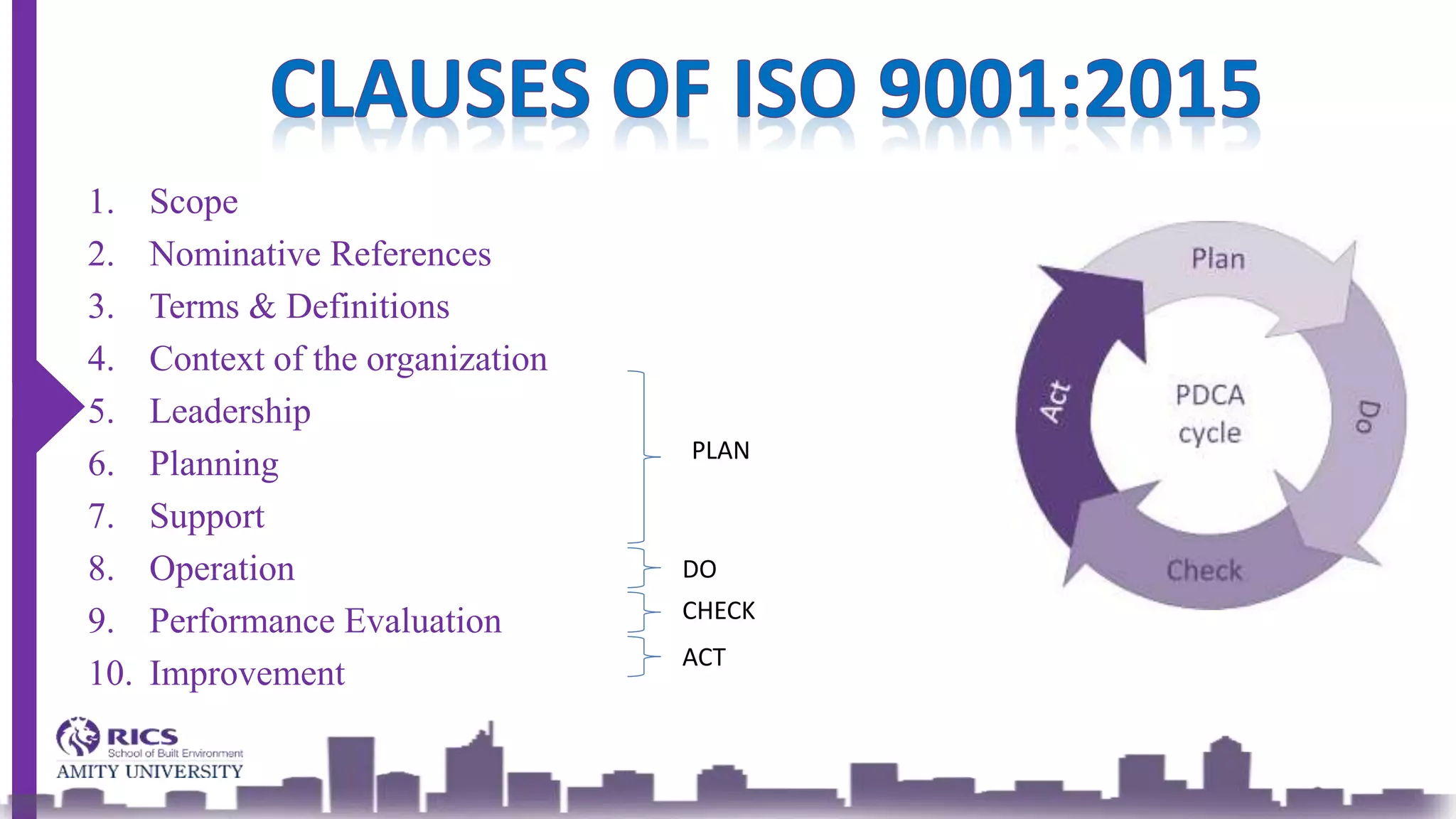
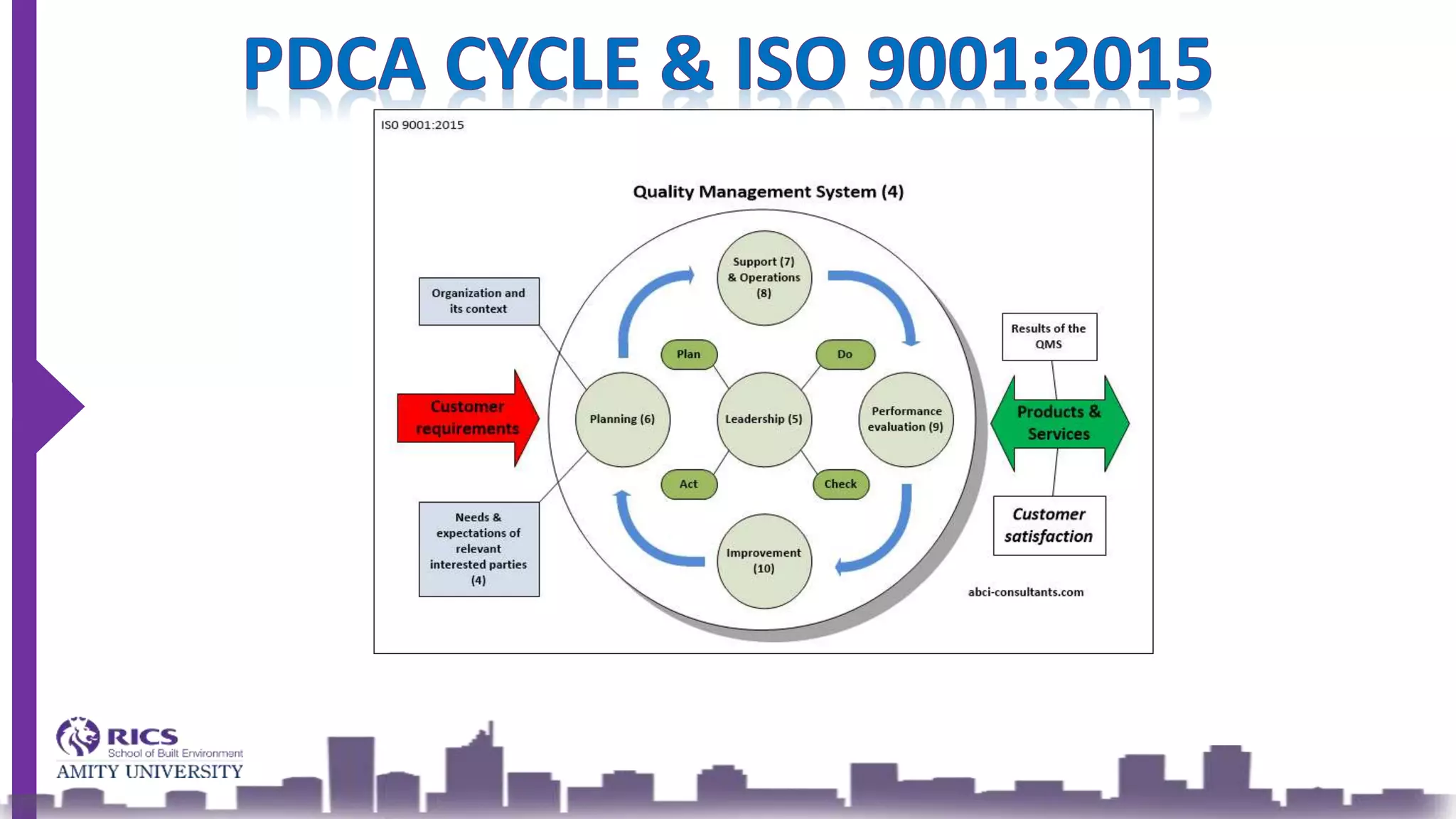
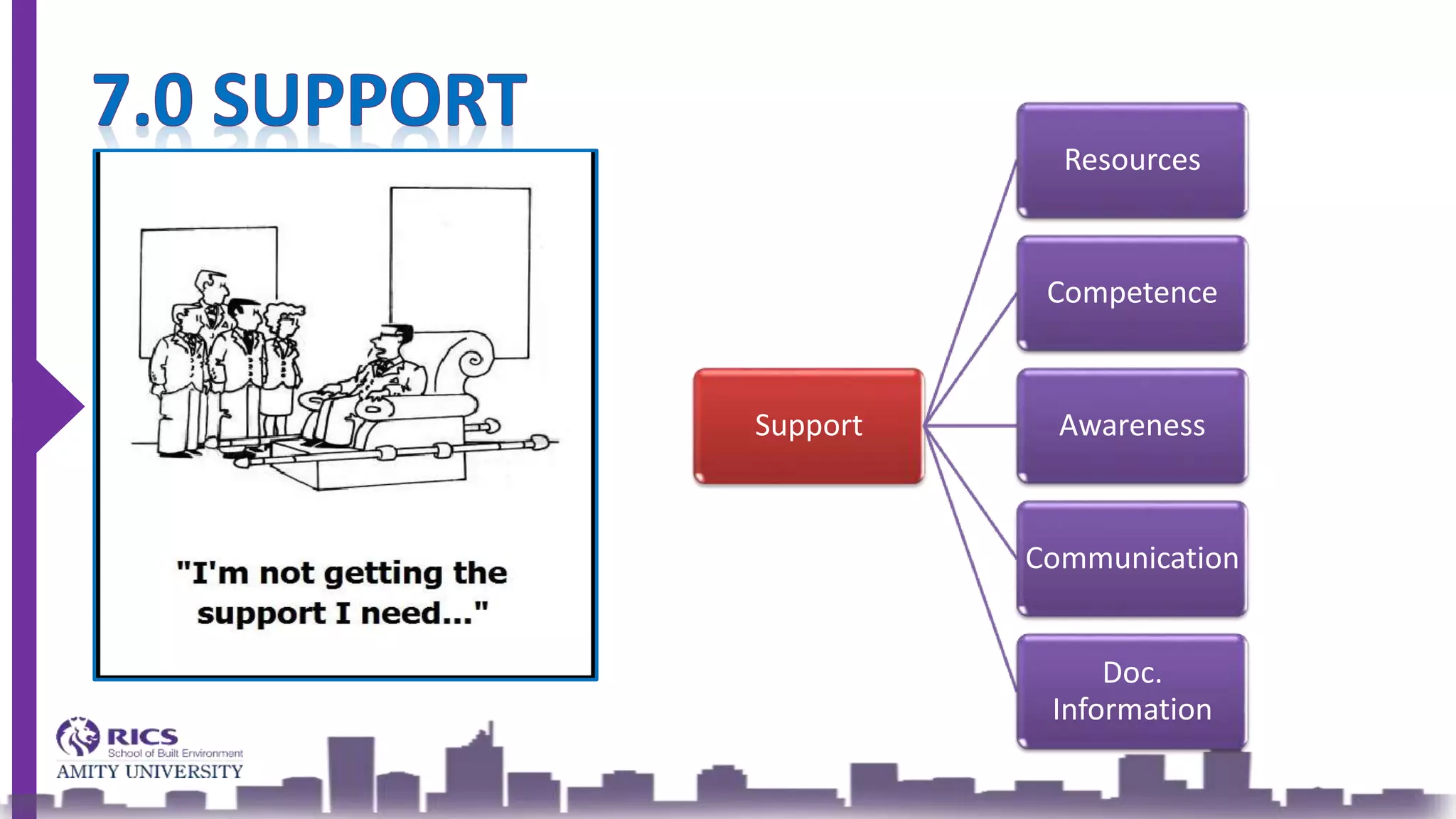
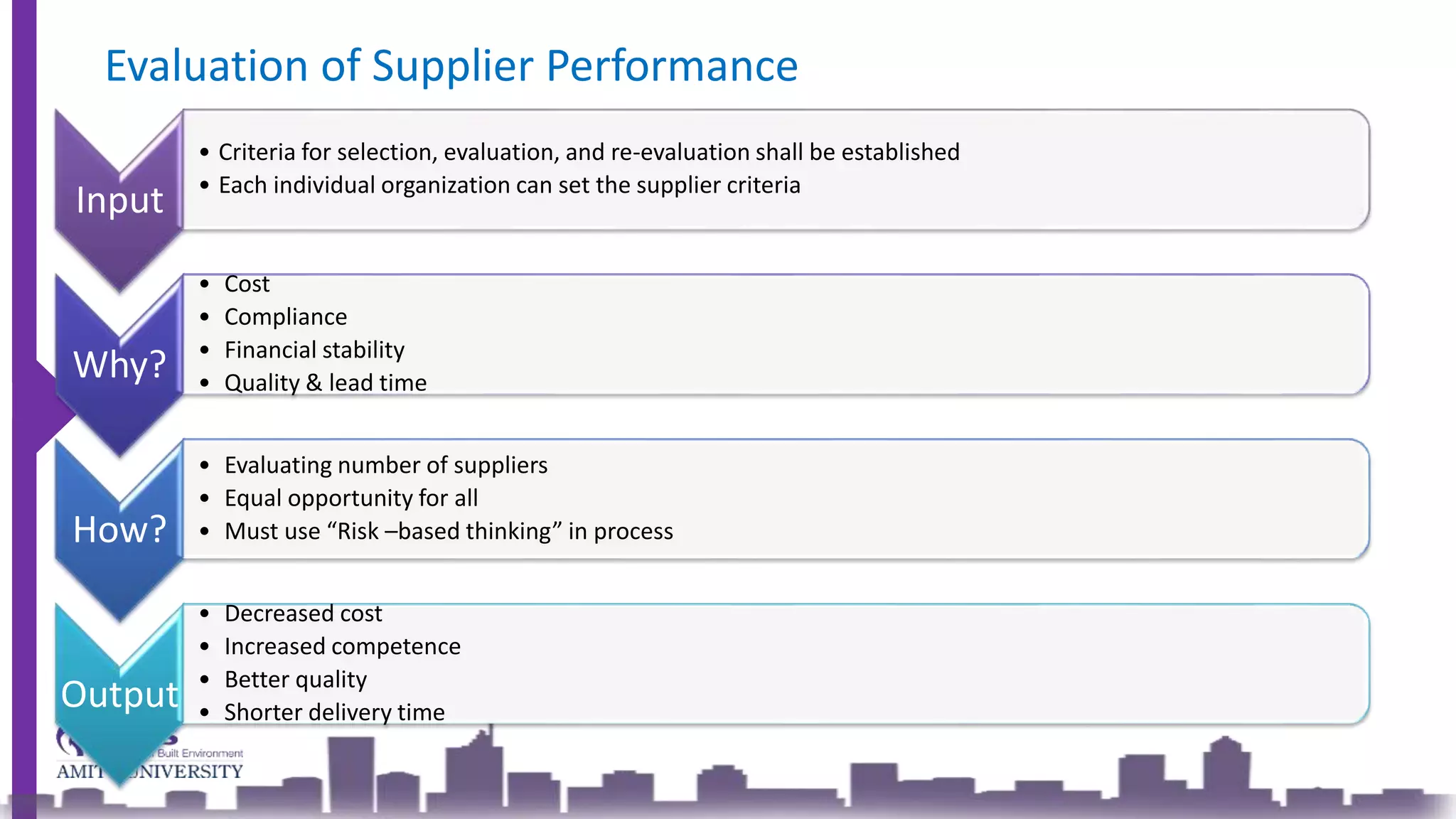
ISO 9001 is an international standard outlining requirements for a Quality Management System (QMS) aimed at improving organizational processes and efficiency while fostering continual improvement. The 2015 version emphasizes leadership, customer satisfaction, and risk management, integrating a structured approach to planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement. The goal is to enhance product quality, reduce non-conformities, and meet customer needs effectively.