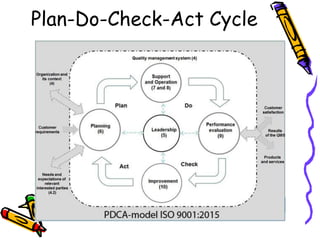
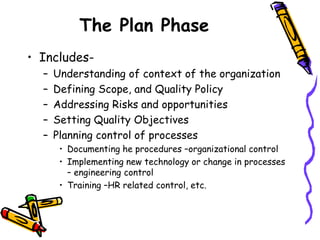
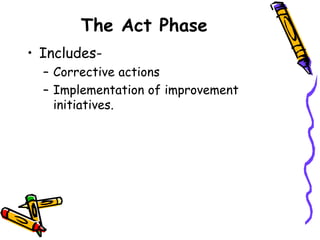
This document provides an overview of ISO 9001:2015. It discusses what ISO means, the benefits of ISO standards, quality management principles, the PDCA cycle, and the structure and requirements of ISO 9001:2015. The key points are that ISO establishes internationally recognized standards, ISO 9001 specifies requirements for quality management systems, and the standard comprises 11 clauses that cover the PDCA cycle of plan, do, check, act for continuous improvement.