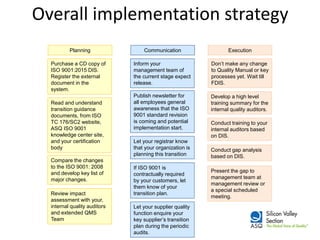
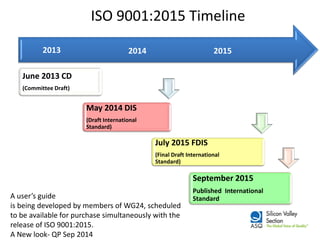
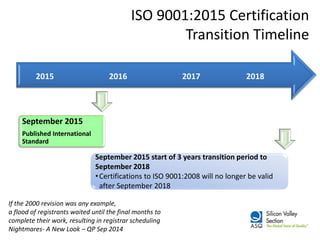
The ISO 9001:2015 revision emphasizes a broader scope of 'products and services', including increased customer focus and risk-based thinking, reflecting the complexities of modern supply chains and stakeholder expectations. Key changes include the adoption of a high-level structure, reduced emphasis on documentation, and enhanced leadership requirements, aiming to improve organizational context and customer satisfaction. Organizations transitioning from ISO 9001:2008 are advised to conduct gap analysis, develop implementation plans, and provide training ahead of the mandatory transition deadline in September 2018.