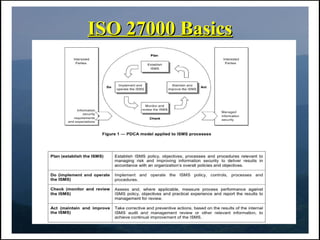
This document provides an introduction to ISO/IEC 27000, which is a family of standards related to information security management systems (ISMS). It discusses why organizations implement ISO 27001 and become certified. Key points covered include how ISO 27001 provides a framework to manage information security risks, helps comply with legal/regulatory requirements, and can provide a competitive advantage for organizations. The document also distinguishes between IT security and information security, and covers basic concepts such as how ISO 27001 relates to asset management and risk assessment.