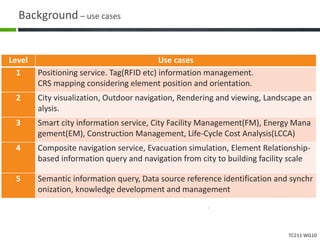
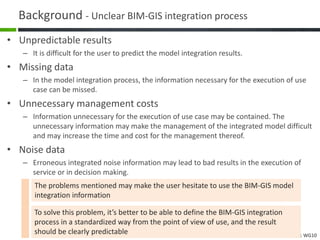
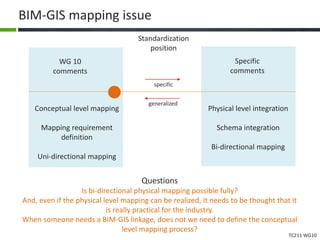
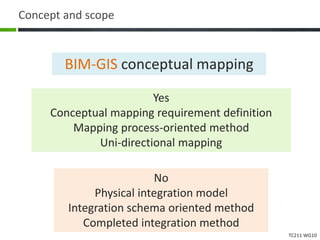
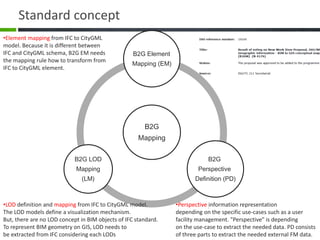
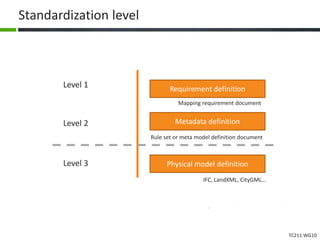
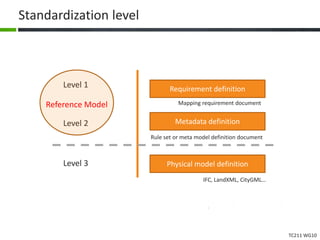
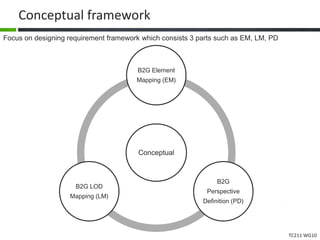
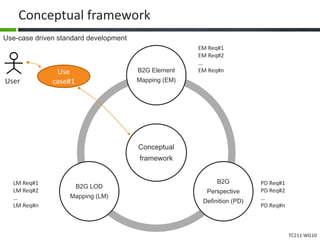
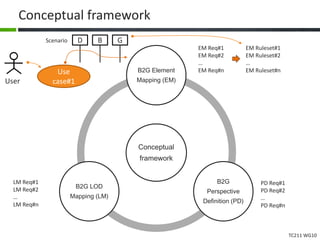
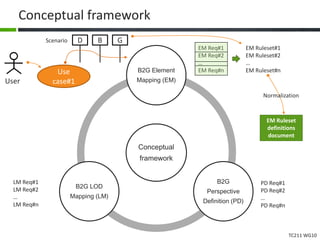
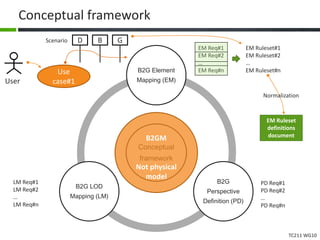
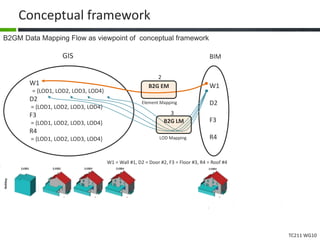
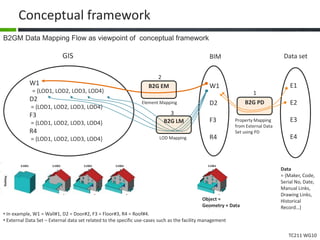
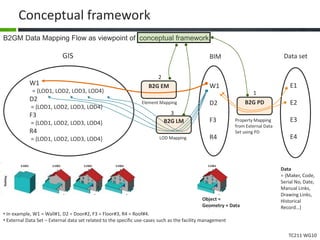
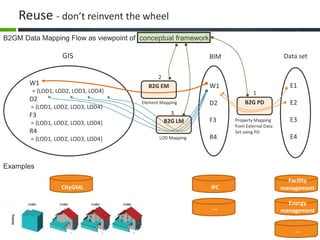
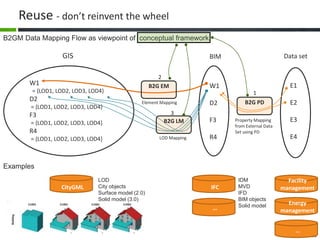
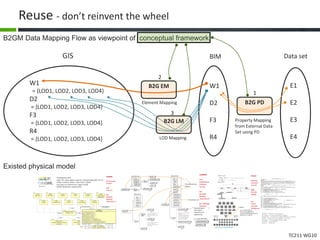
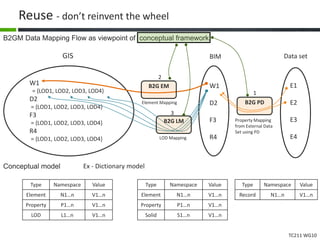
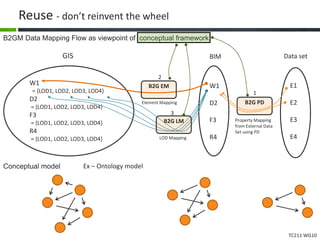
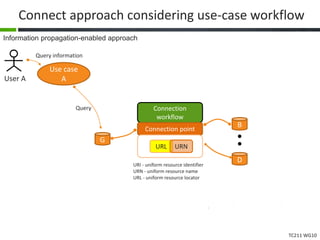
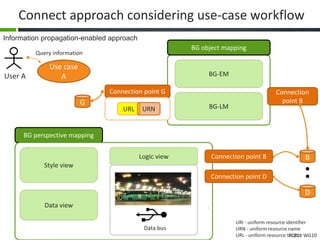
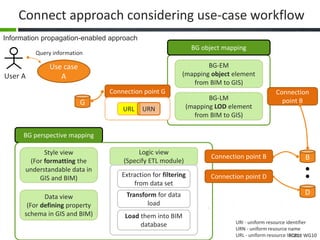
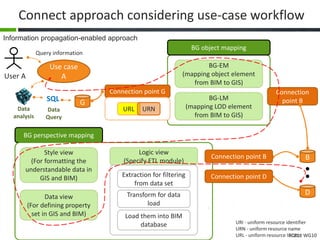
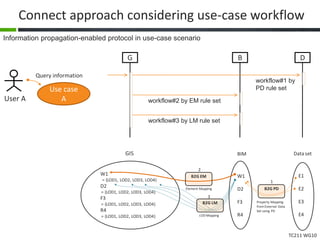
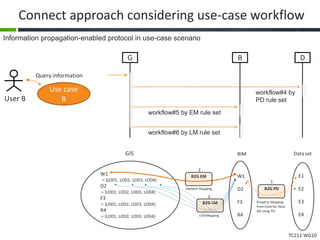
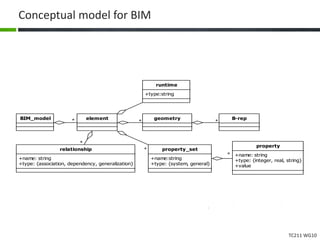
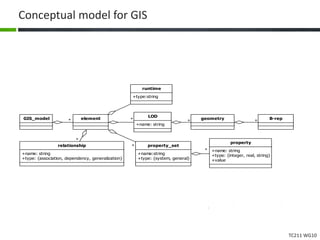
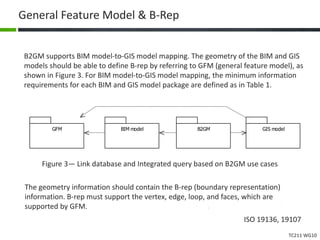
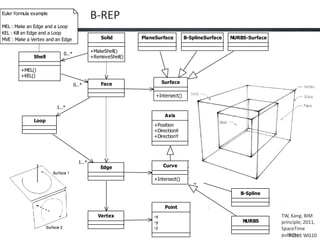
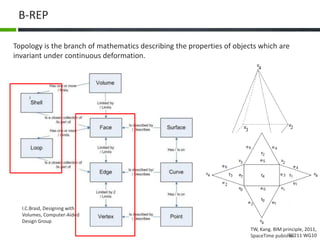
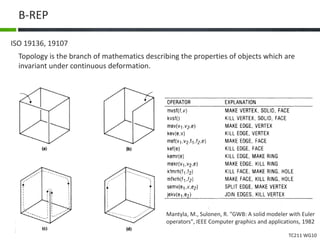
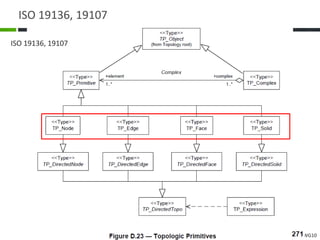
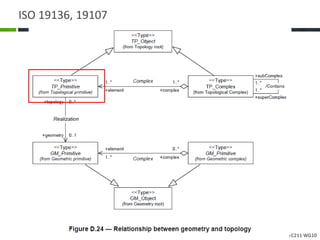
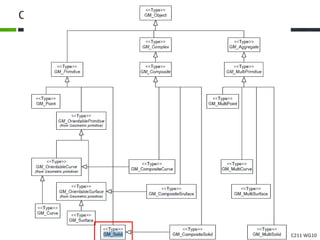
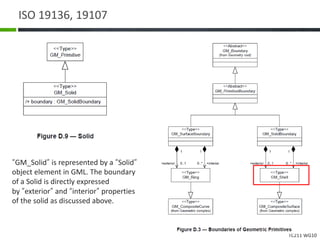
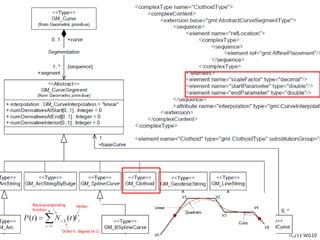
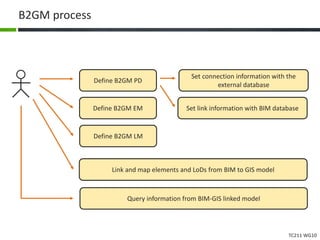
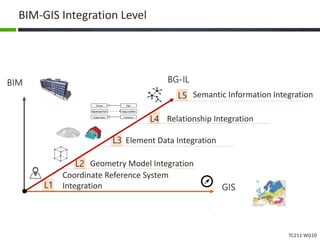
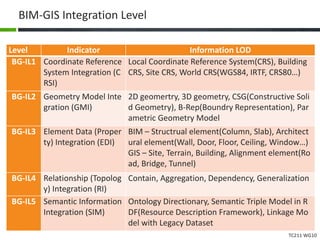
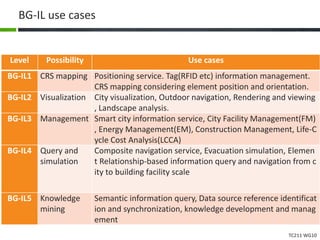
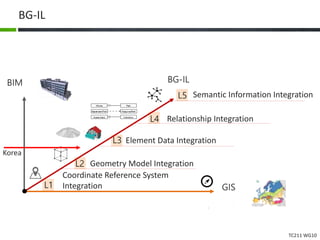
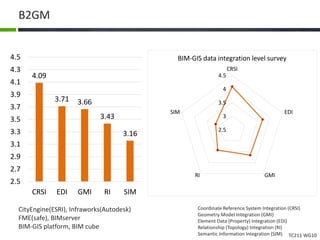
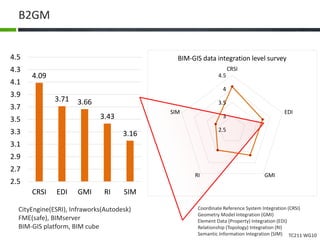
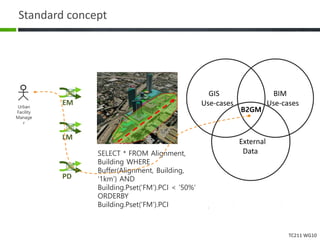
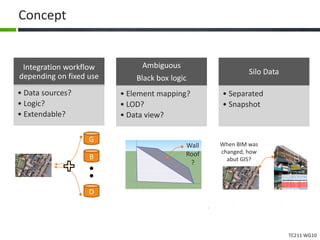
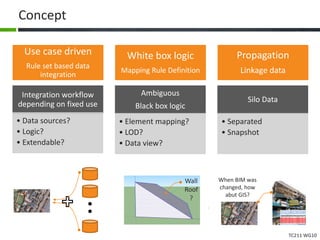
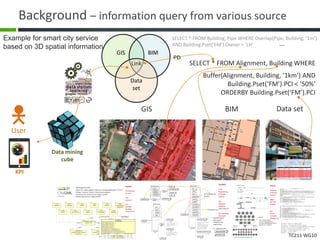
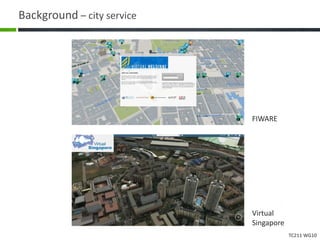
This document proposes a conceptual framework for the ISO 19166 B2GM standard, which defines a conceptual mapping process between building information models (BIM) and geospatial information models (GIS). The framework focuses on defining mapping requirements through three parts: element mapping, level-of-detail mapping, and perspective definition. It is intended to standardize the conceptual mapping process in a use-case driven manner without requiring full physical data integration. The framework is designed to reuse concepts from existing BIM, GIS, and related standards to avoid reinventing concepts.