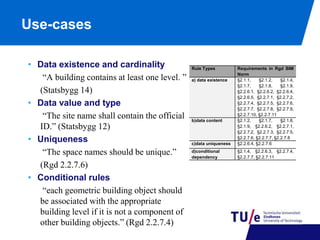
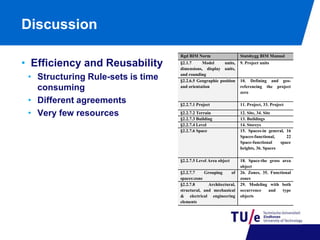
This document discusses model view checking, an automated validation method for building information models (BIMs) that uses rules to check for compliance with interoperability and exchange requirements. It presents research on developing an open-source IFC validation tool based on open standards. The tool structures rulesets using the BIM Collaboration Format and generates reports. Use cases demonstrate checking for data existence, value/type, uniqueness, and conditional rules. Ongoing work involves implementing the tool as a plugin for BIM servers and expanding the expressivity and standardization of rule libraries.

![Background
• Interoperability Requirements
• IFC Validation
• Exchange Requirements
• Business Rules
E.g. “A project must have a site.”
IfcProject
(INV) IsDecomposedBy [1:1 ]
IfcRelAggregates
RelatedObjects [1:1]
IfcSite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecppm2014presentation-140924045425-phpapp01/85/Ecppm2014-presentation-2-320.jpg)
![Related Research
Coordination View
IfcProject
(INV) IsDecomposedBy [1:1 ]
IfcRelAggregates
RelatedObjects [1:1]
IfcSite
COBie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecppm2014presentation-140924045425-phpapp01/85/Ecppm2014-presentation-3-320.jpg)
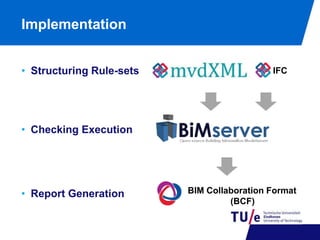
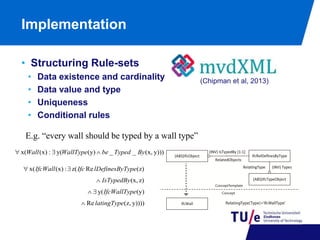
![Implementation
• Checking Execution
• Report Generation
(INV) IsTypedBy [1:1]
IfcWall IfcRelDefinesByType
RelatingType [1:1]
IfcWallType
BIM Collaboration Format](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecppm2014presentation-140924045425-phpapp01/85/Ecppm2014-presentation-7-320.jpg)