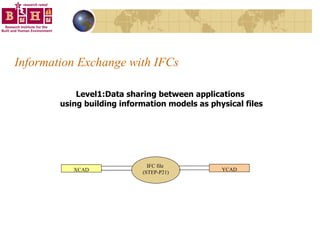
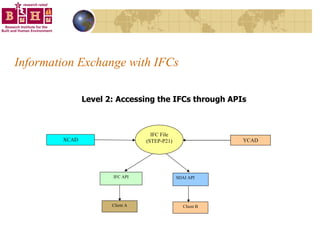
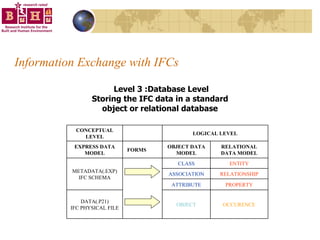
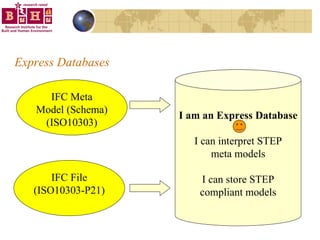
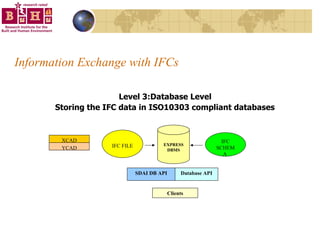
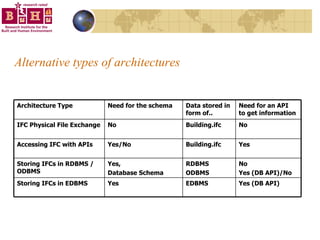
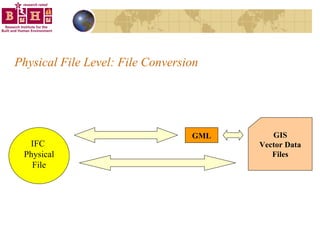
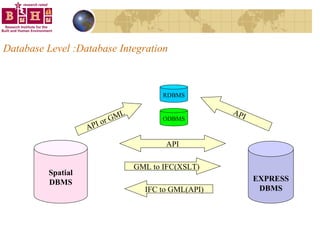
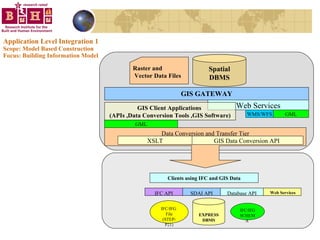
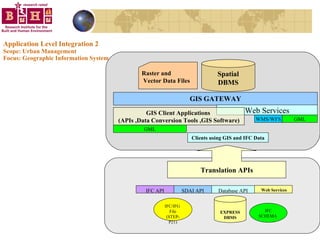
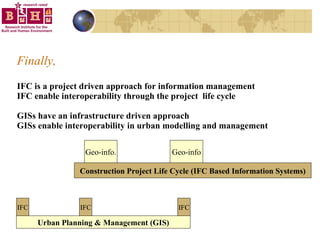
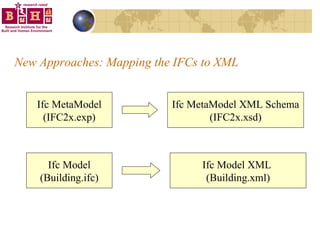
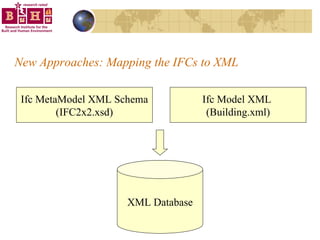
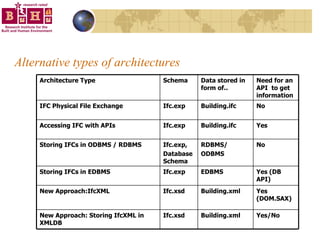
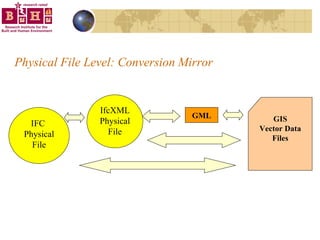
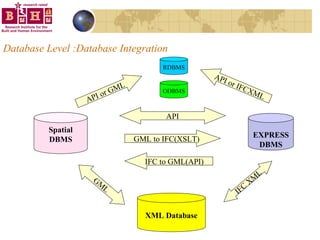
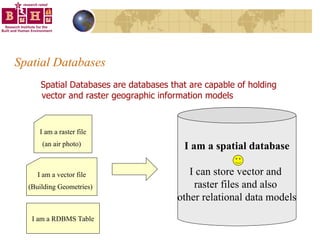
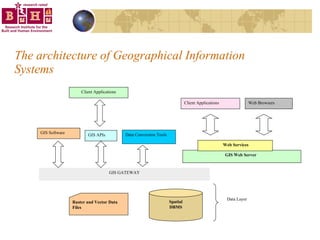
The document discusses integrating building information models (BIM) with geographic information systems (GIS). It outlines several challenges with information exchange between different software used in construction and urban management. It then reviews potential approaches to integration including using standards like IFC and GML, mapping data to common data models, and different system architectures like using application programming interfaces (APIs), physical file exchange, or storing data in databases.













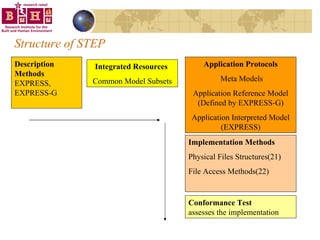
![IFC Schema = The Meta Model Meta Model file is called IFC Schema Meta Model file holds the IFC entities IFC entities contain descriptive information about IfcObjects. Meta Model is defined by EXPRESS The meta model file has the .exp extension ENTITY IfcOrganizationRelationship; Name : IfcLabel; Description : OPTIONAL IfcText; RelatingOrganization : IfcOrganization; RelatedOrganizations : SET [1:?] OF IfcOrganization; END_ENTITY;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irw2004v4-12785890193106-phpapp01/85/IRW-2004-19-320.jpg)