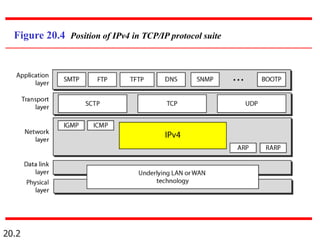
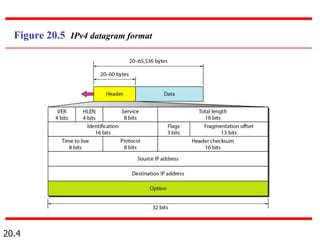
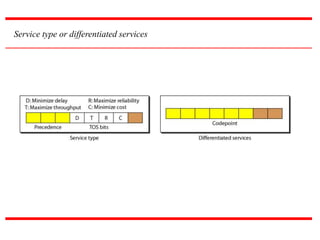
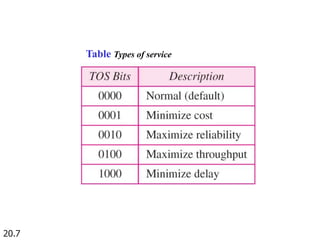
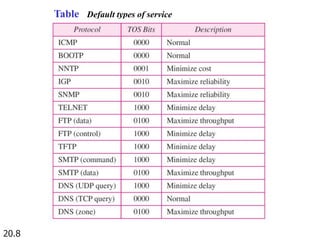
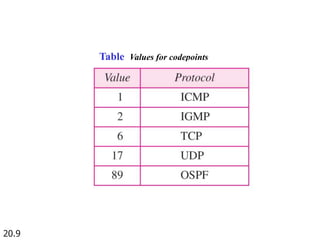
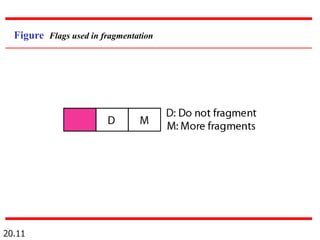
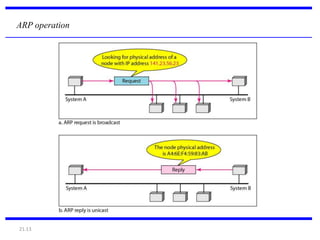
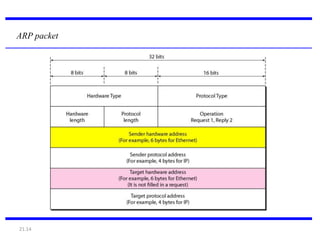
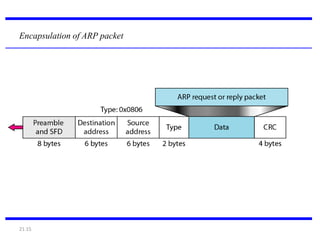
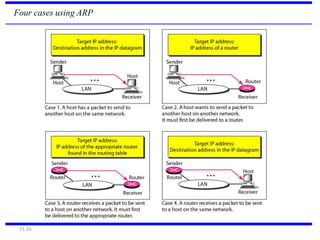
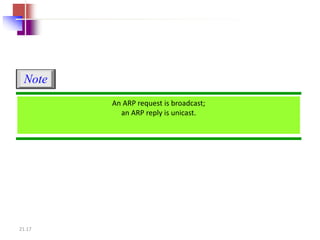
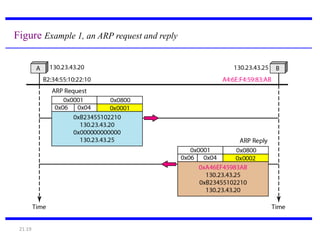
IPv4 is the delivery mechanism used by TCP/IP protocols to transmit data in packets called datagrams. It is an unreliable, connectionless protocol that does not guarantee delivery and provides no error or flow control. IPv4 operates at the host-to-host network layer and uses a datagram approach for packet switching networks. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) maps logical IP addresses to physical hardware addresses to allow communication between hosts on the same local area network. ARP uses broadcast for requests and unicast for replies.